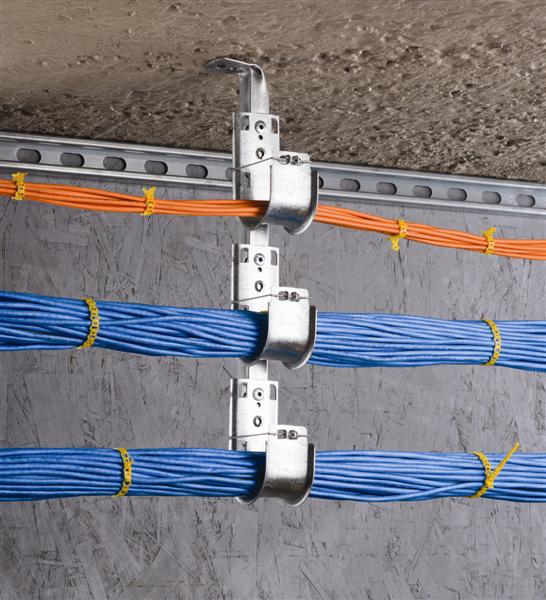
No matter where your cables are set, keeping them in good protection is always helpful for extending the cable service life. As we know, it is more difficult to arrange the harness cable due to the multiple strings. However, a better protection and management is necessary all the time. Thus, a cable manager named wire loom is designed to meet the demands. This device efficiently arranges and protects the cables at the same time. A growing number of applications are adopting the wire looms for harness cable routing.
Wire loom, also known as convoluted tube, is a corrugated pipe-shaped cable organizer widely used for cable harness protection. It can be made of several materials, such as polyamide (PA), polyester (PET), polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polyurethane (PUR) and elastomer. You can find the applications in a variety of industries, including automotive, agriculture, construction, marine and telecommunications. The inside diameter is also optional to suit the size of cables, and common diameters are 3/8”, 1/4”, 3/4”, 1/2”, 1” etc. The following picture shows the general look.
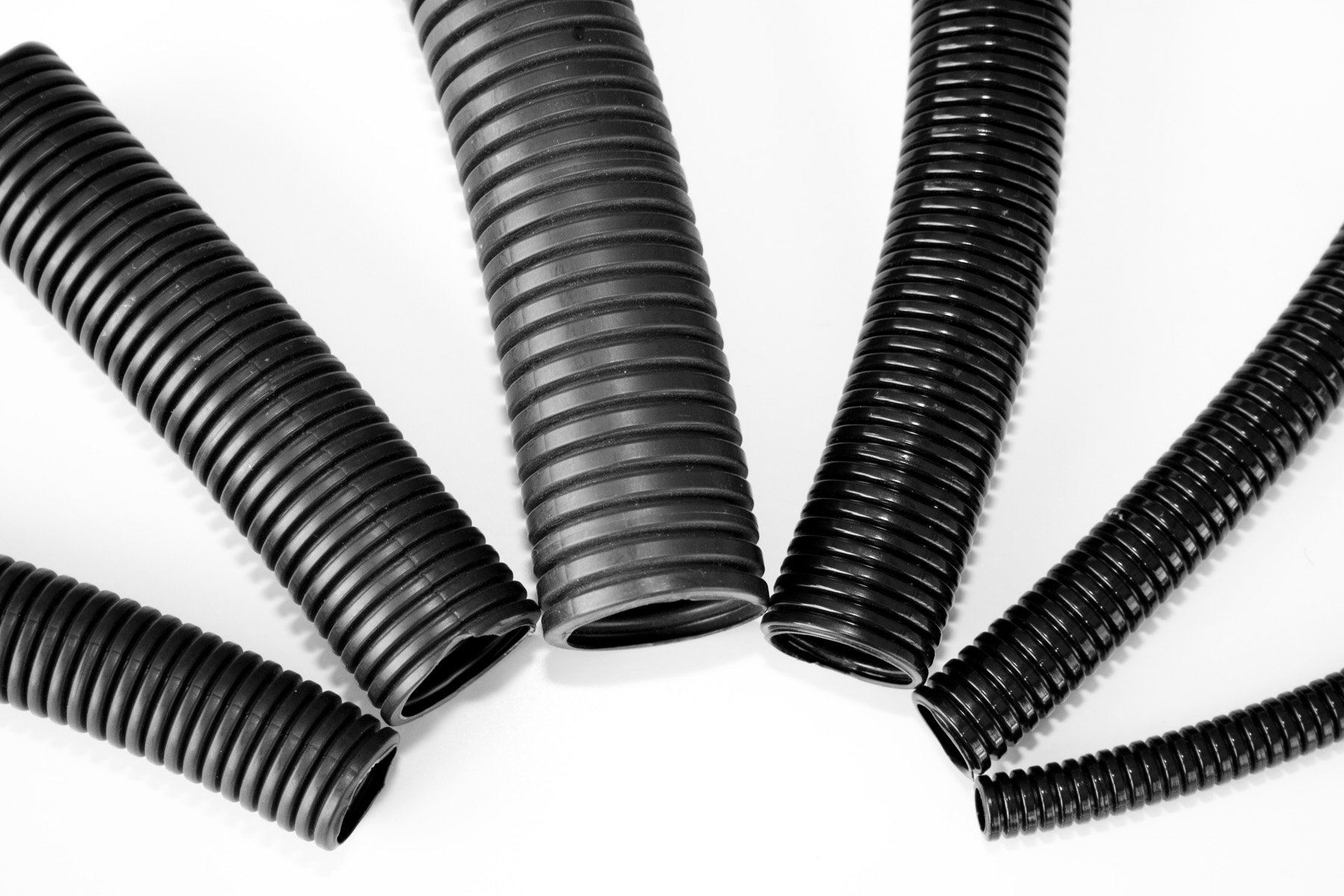

There are three aspects that you can consider when selecting the wire loom. Firstly, you can look over the design of wire loom to decide whether it needs to be split, non-split, spiral wrap or self-wrapping. Typically, split ones are the standard type preferred by most applications. Secondly, as mentioned above, the size is optional, thus you need to choose the right size to fit your wires. You can measure the wire bundle diameter in advance and then make sure it to be a little larger than the wire bundle. Thirdly, you should select the material based on the installation environment so as to give better protection for the cables. Temperature, moisture, chemical, vibration and other elements can all be taken into consideration during the selection.
It is surly a cost-effective solution to use wire loom for cable harness protection. The install and removal of is very flexible and easy, especially for split wire loom. Most importantly, it is resistant to various abrasions (friction, vibration, fraying and puncture), fluids (automotive fluids, water, snow, salt and ice) and weathers ( heat, cold and sunlight). Apart from these, using it also ensures the cable management to be neat and clean, which is important to the higher performance of cables.
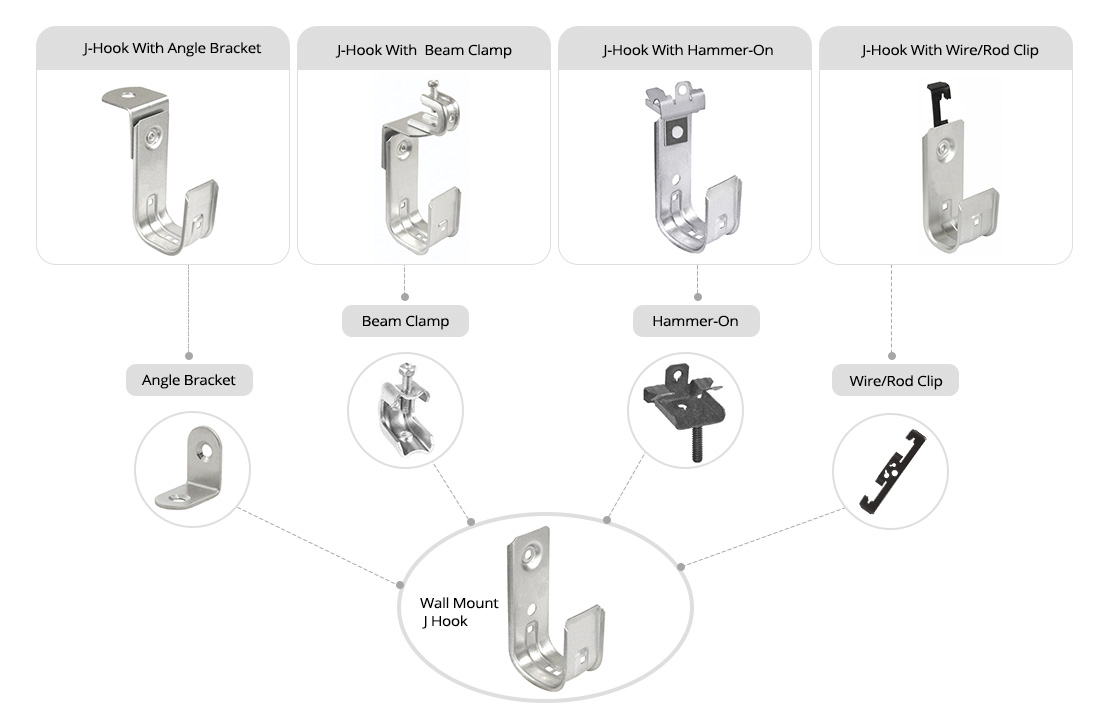
Besides the standard wire looms, there are also other related products that can provide easier deployment.
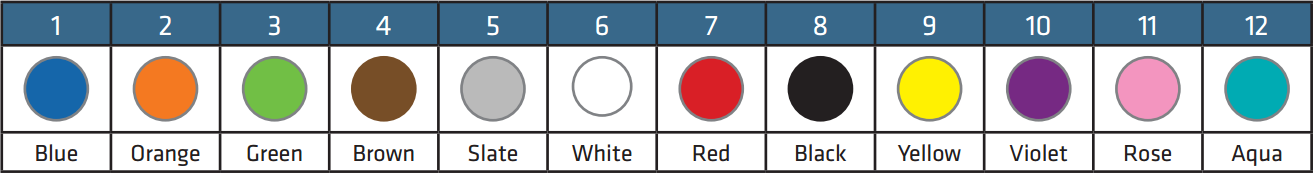
The typical color is black, but there are also other color choices, such as red, white, blue, yellow and so on. These colored wire looms can be seem as the ornament for the installation area, especially when the they are used at people’s houses. In addition, it is simpler to distinguish different cable bundles when multiple wire looms are used in the same place.

Wire loom connector, namely wire loom tee, is used to offer safe branching of cables. It can connect three pieces of wire looms with a simple snap. The nylon and TPE rubber material designs secure the junction area to be protected from high temperature and abrasion. Different branch diameters are also available within one connector to provide convenience for the connection of different size.

If you are seeking for a better protection for your fiber cable, wire loom is an ideal solution that can be used for all kinds of cabling applications. FS.COM provides different colors and sizes of wire looms and connectors. Please visit our website for more detailed information if interested.