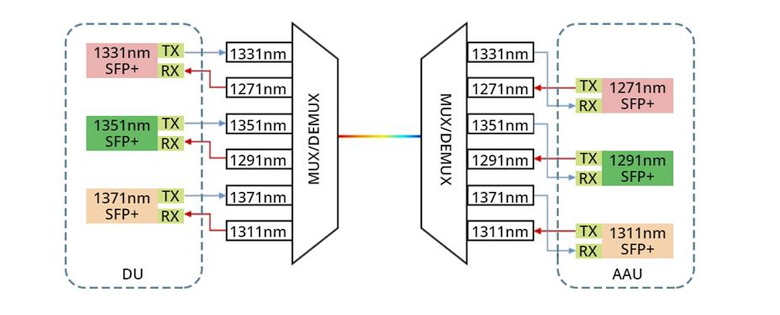
As the demand for faster data transfer continues to surge, 800G transceivers are garnering attention for their high bandwidth, rapid transfer rates, superior performance, high density, and future compatibility. In this article, we will offer an overview of the different types of 800G optical modules, explore their applications, and address some frequently asked questions to assist you in making an informed choice when selecting an 800G transceiver.
Types of 800G Transceiver
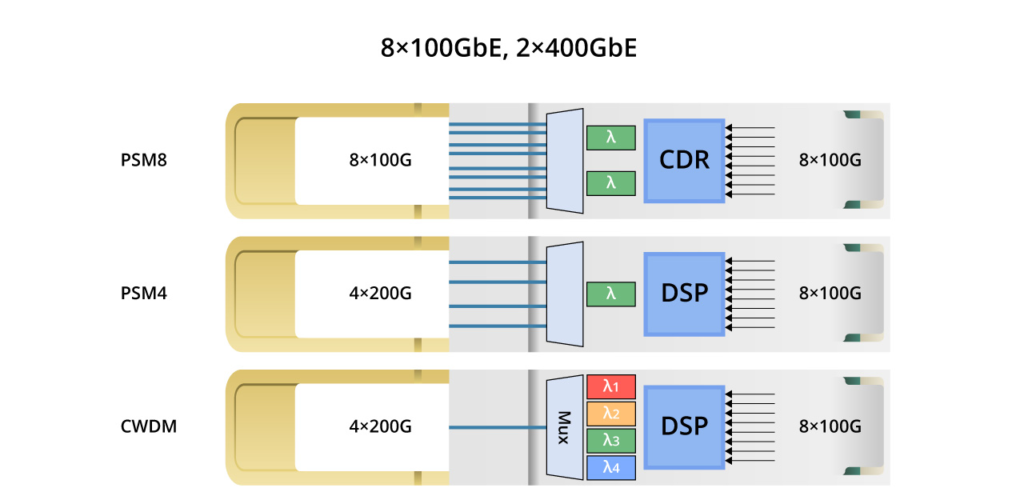
800G = 8 x 100G = 4 x 200G. Therefore, based on the single-channel rate, 800G transceivers can be broadly categorized into two groups: single-channel 100G and 200G. The diagram below illustrates the corresponding architectures. Single-channel 100G optical modules can be implemented relatively swiftly, whereas 200G optical modules entail greater demands on optical devices and necessitate a gearbox for conversion. This article primarily focuses on introducing single-channel 100G modules.
Single-Mode 800G Transceivers
The 800G single-mode optical transceiver is suitable for long-distance optical fibre transmission and can cover a wider network range.
800G DR8, 800G PSM8 & 800G 2xDR4
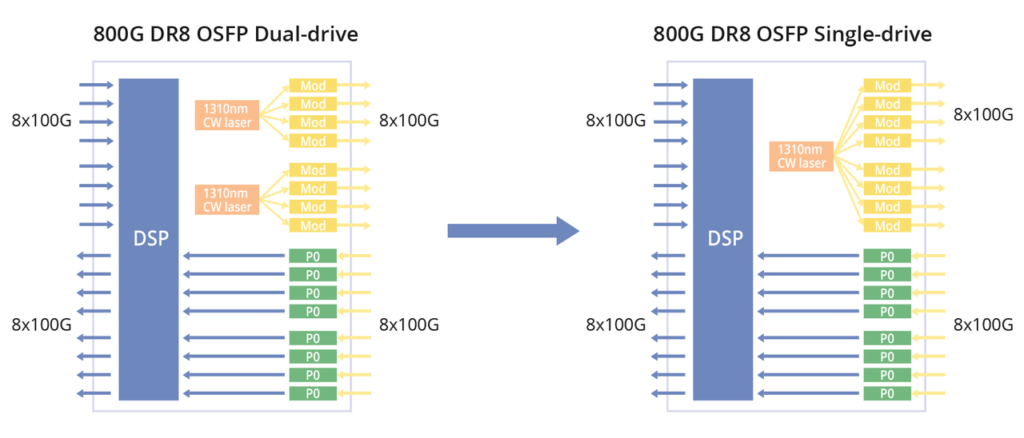
The three standards share a similar internal architecture, featuring 8 Tx and 8 Rx with a single channel rate of 100 Gbps and require 16 optical fibres.
800G DR8 optical module uses 100G PAM4 and 8-channel single-mode parallel technology, and the transmission distance through single-mode optical fibre can reach up to 500m, which is typically used in data centres, 800G-800G, 800G-400G, and 800G-100G interconnections. FS 800G QSFP-DD DR8 delivers exceptional performance for 800GBASE Ethernet applications, offering throughput of up to 800 Gigabits per second over eight pairs of single-mode fibres (SMF) with MPO-16 APC connectors, extending up to 500 metres. Fully compliant with IEEE P802.3ck, IEEE 802.3cu, and QSFP-DD MSA standards, this transceiver ensures seamless compatibility and reliable operation.
800G PSM8 utilises CWDM technology with 8 optical channels, each delivering 100Gbps, supporting 100m transmission distance, making it ideal for long-distance transmission and fibre resource sharing.
800G 2FR4/2LR4/FR4/FR8
800G FR and LR in these designations stand for Fixed Reach and Long Reach, representing fixed and long transmission distances, respectively.
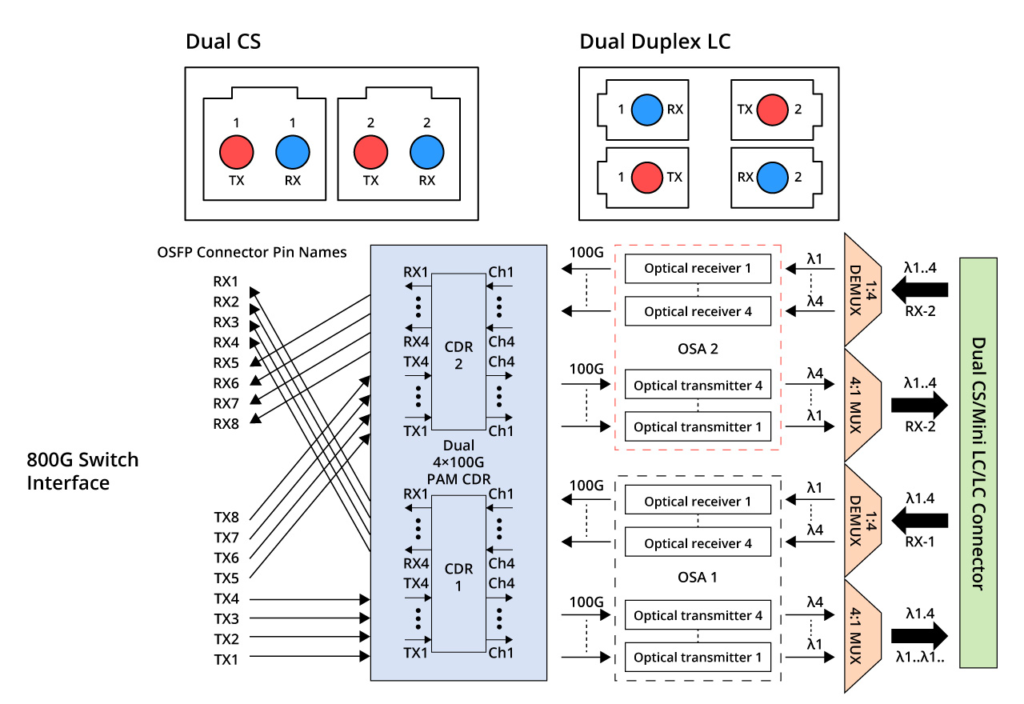
800G 2xFR4 and 800G 2xLR4 are two additional standards with similar internal structures. They comprise 4 wavelengths operating at a single-channel rate of 100 Gbps. By utilizing Mux, the number of required optical fibres is reduced to 4, as depicted in the figure below. These standards were introduced as upgrades to the 400G FR4 and LR4 transceivers. They employ CWDM4 wavelengths at 1271/1291/1311/1331nm. 800G 2xFR4 supports a transmission distance of 2km, while 800G 2xLR4 supports a transmission distance of 10km. Optical interfaces for these standards utilise dual CS or dual duplex LC interfaces. They are both suitable for 800G Ethernet, breakout 2x 400G FR4/LR4, data centres, and cloud networks.
FS provides 800G 2xFR4 and 800G 2xLR4 modules in OSFP packages. FS 800G 2FR4 optical transceiver Module is designed for 800GBASE Ethernet throughput up to 2km over single-mode fibre (SMF) with duplex LC connectors. FS 800G 2LR4 transceiver supports up to 10km link lengths over single-mode fibre (SMF) via dual LC connectors. Both products have undergone rigorous testing and have excellent performance.
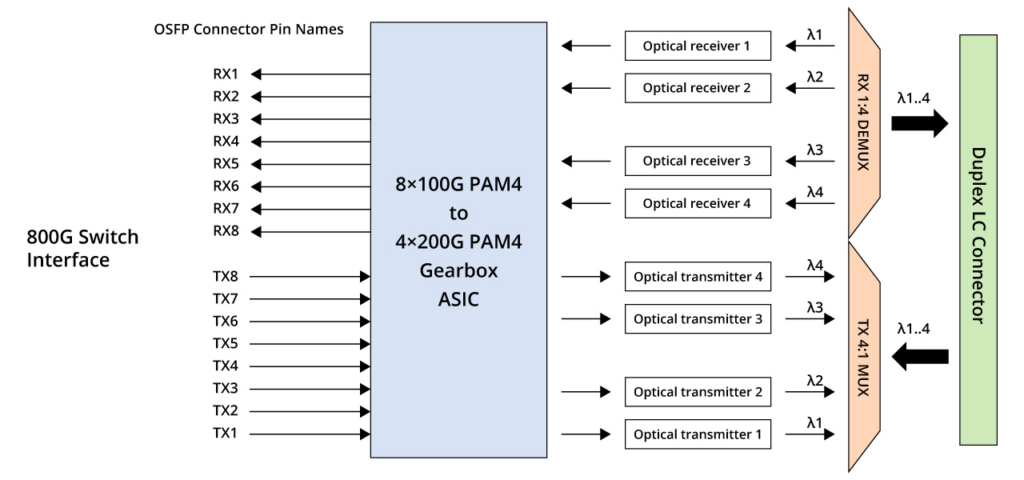
800G FR4 adopts a scheme employing four wavelengths and PAM4 technology, operating at a single-channel rate of 200 Gbps and necessitating two optical fibres, as depicted in the figure below. It sustains a transmission distance of 2km and is commonly employed in data centre interconnection, high-performance computing, storage networks, and other applications.
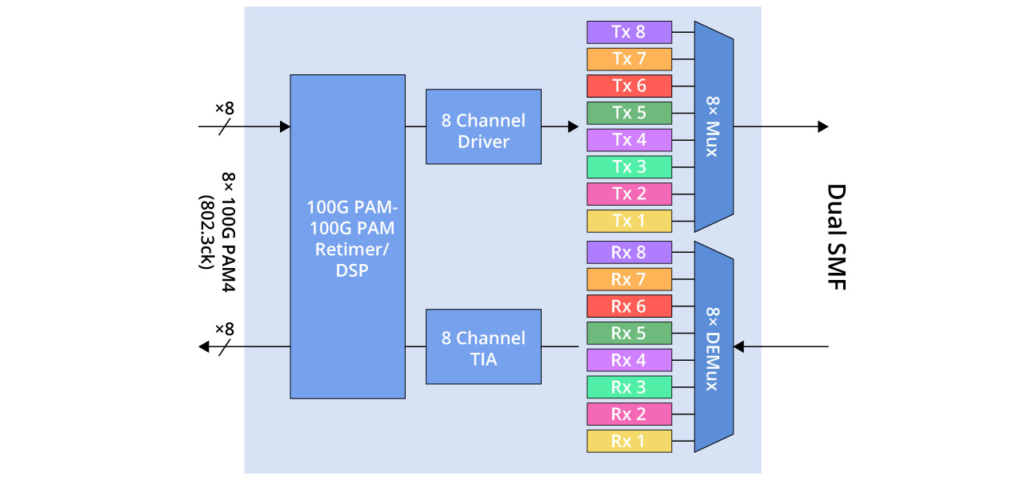
Finally, 800G FR8 utilises eight wavelengths, each operating at a speed of 100 Gbps, as illustrated in the figure below. It necessitates two optical fibres and supports a transmission distance of 2km. Additionally, 800G FR8 can offer increased transmission capacity. Typical applications include wide-area networking, data centre interconnection, and so forth.
Multimode 800G Transceivers
There are primarily two standards for 800G optical transceivers used in multimode applications when the transmission distance is under 100 meters.
800G SR8
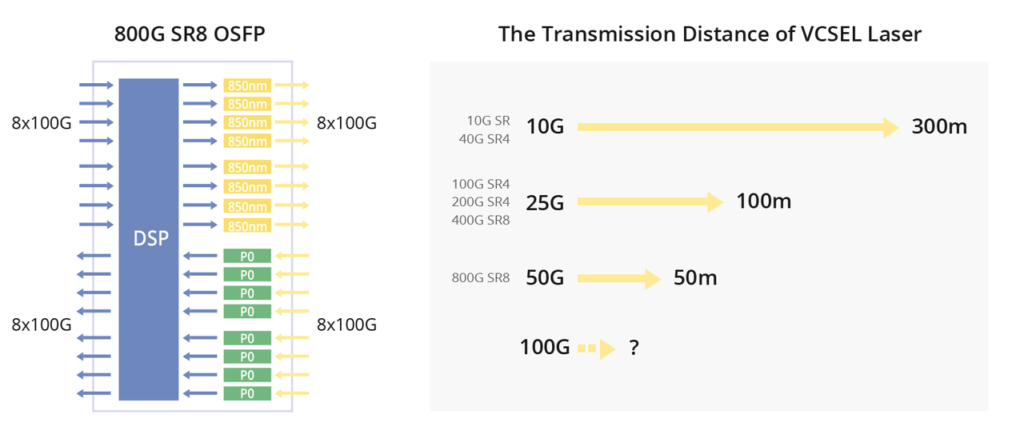
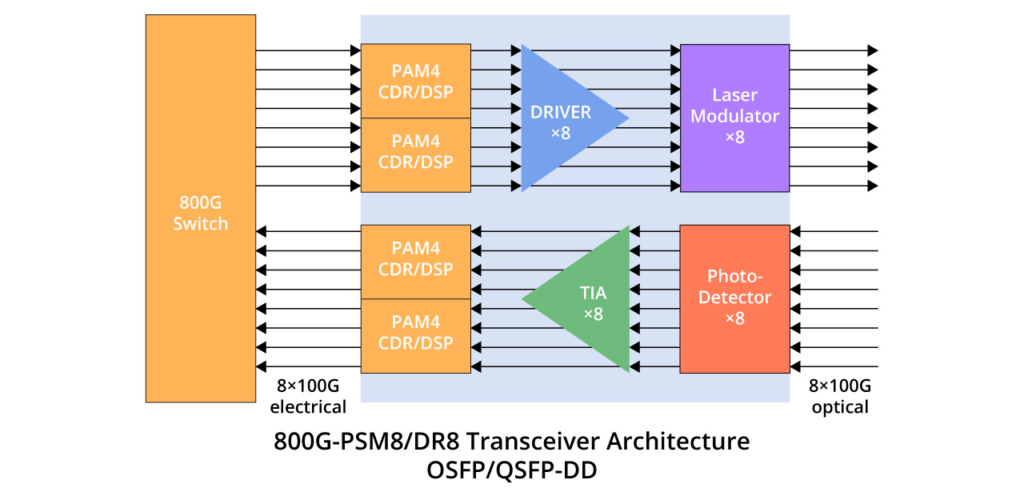
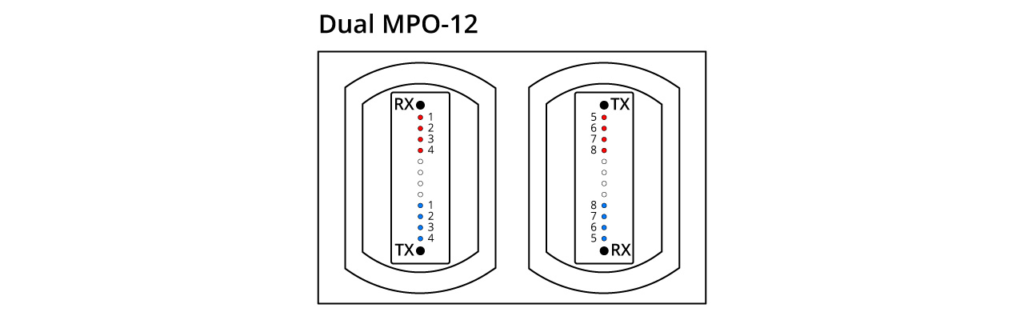
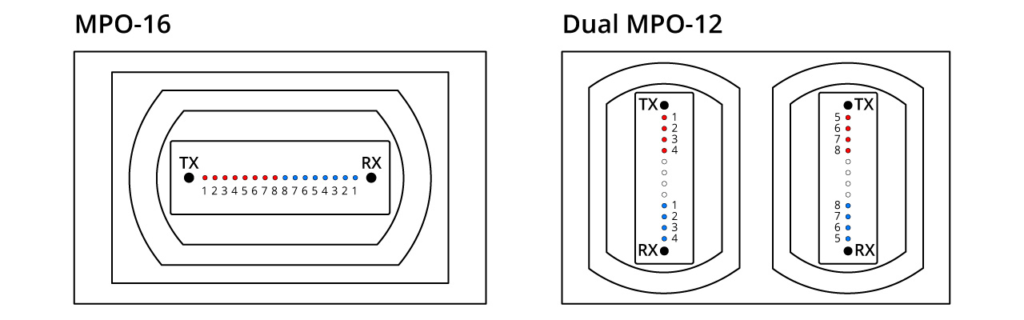
The 800G SR8 transceiver adopts the VCSEL technology with a wavelength of 850nm and a single-channel rate of 100Gbps PAM4. It necessitates the use of 16 optical fibres. This can be regarded as an enhanced version of the 400G SR4, featuring twice the number of channels. The transceiver employs either an MPO16 or a Dual MPO-12 optical interface, as depicted in the diagram provided. OSFP 800G SR8 optical modules are generally used for 800G Ethernet, data centre links, or 800G-800G interconnection.
The FS OSFP 800G SR8 optical transceiver has a built-in Broadcom 7nm DSP chip with a maximum power consumption of 15W, providing high speed and low power consumption in 800G links. The top-fin OSFP is used in Quantum-2 air-cooled switches and is suitable for use in InfiniBand NDR end-to-end systems. It is also perfectly compatible with NVIDIA QM9700/9790 devices for seamless integration into compute and storage infrastructures, ensuring efficient high-performance interconnections.
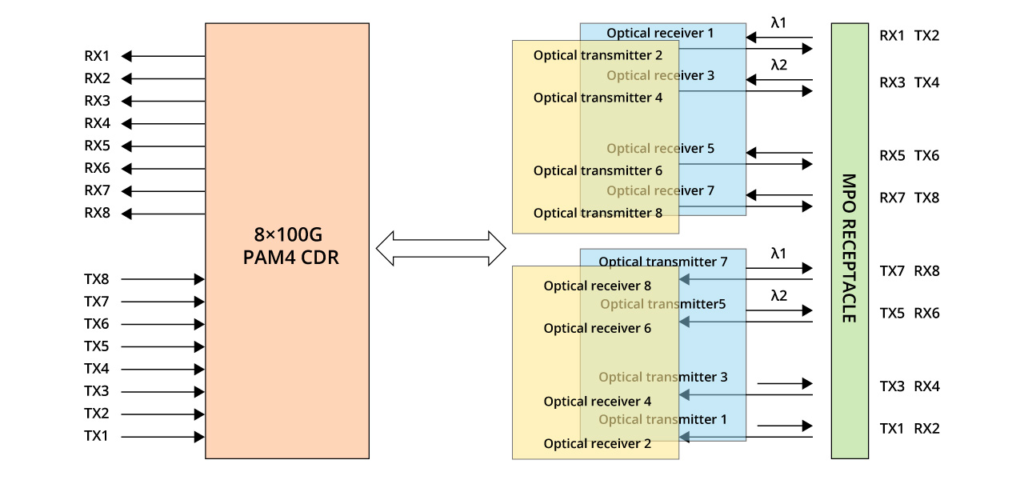
800G SR4.2
This scheme utilises two wavelengths, 850nm and 910nm, enabling bidirectional transmission over a single fibre, commonly referred to as bi-directional transmission. The module incorporates a DeMux component to separate the two wavelengths. With a single-channel rate of 100 Gbps PAM4, it requires a total of 8 optical fibres, which is half the amount needed for SR8.
Applications of 800G Transceiver
In the realm of high-performance networking, the evolution of 800G transceivers has ushered in a new era of possibilities.
Data Centre Connectivity
Data Centre Interconnectivity is one of the primary domains where the prowess of 800G optical modules shines. With InfiniBand, these modules facilitate seamless communication between data centres, powering the backbone of modern interconnected infrastructures.
High-Performance Computing
In the arena of High-Performance Computing, where processing demands are ceaselessly escalating, the efficiency of 800G transceives becomes a game-changer. Modules ensure fast data transfer, reduce latency, and optimize overall system performance.
5G and Communication Networks
The proliferation of 5G and communication networks demands not only speed but also reliability. Enter 800G QSFP and QSFP-DD transceivers, engineered to meet the needs of next-generation communication networks. Their advanced capabilities underpin the 5G architecture, ensuring a robust and responsive network infrastructure.
Conclusion
As a key component of next-generation high-speed optical communications, 800G optical modules are available in a variety of types to fulfil diverse application requirements. A comprehensive understanding of the types of transceivers, application areas, and answers to common questions about 800G transceivers will facilitate the advancement of data transmission technology. By mastering this advanced technology, we can more effectively adapt to the challenges and opportunities of the digital age.
Related Articles:
Unveiling the Future: The Evolution of 800G OSFP Optical Transceivers
Unlocking Next-Gen Connectivity with the 800G OSFP Transceiver