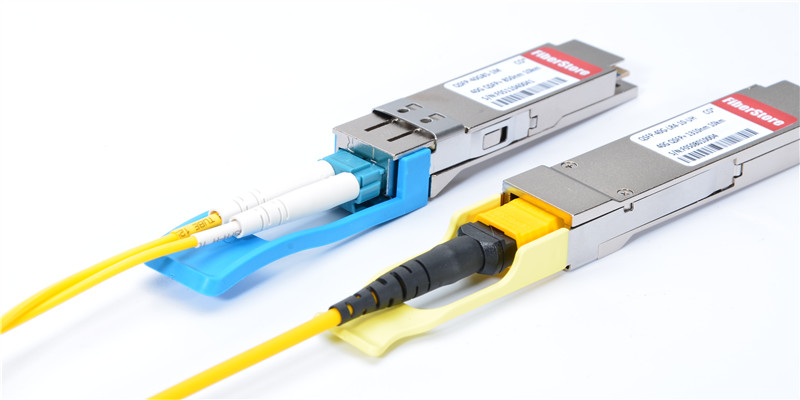
In telecommunication, fiber loopback is a hardware designed to provide a media of return patch for a fiber optic signal, which is typically used for fiber optic testing or network restorations. When we need to know whether our fiber optic transceiver is working perfectly, we can use a fiber loopback cable as an economic way to check and ensure it. Basically, the loopback aids in debugging the physical connection problem of the transceiver by directly routing the laser signal from the transmitter port back to the receiver port. Since fiber optic transceivers have different interface types and connect different types of cables, it is not that simple to choose a right loopback for our transceiver. This post will be a guide on how to choose a right loopback cable for specific transceiver module.
Before deciding which loopback cable to use, we should firstly know the structure and classification of fiber loopback cable. Generally, a fiber loopback is a simplex fiber optic cable terminated with two connectors on each end, forming a loop. Some vendors provide improved structure with a black enclosure to protect the optical cable. This designing is more compact in size and stronger in use. Based on the fiber type used, there is single-mode loopback and multimode loopback, available for different polishing types. According to the optical connector type of the loopback, fiber loopback cables can be divided to LC, SC, FC, ST, MTP/MPO, E2000, etc. In testing fiber optic transceiver modules, the most commonly used are LC, SC and MTP/MPO loopback cables.
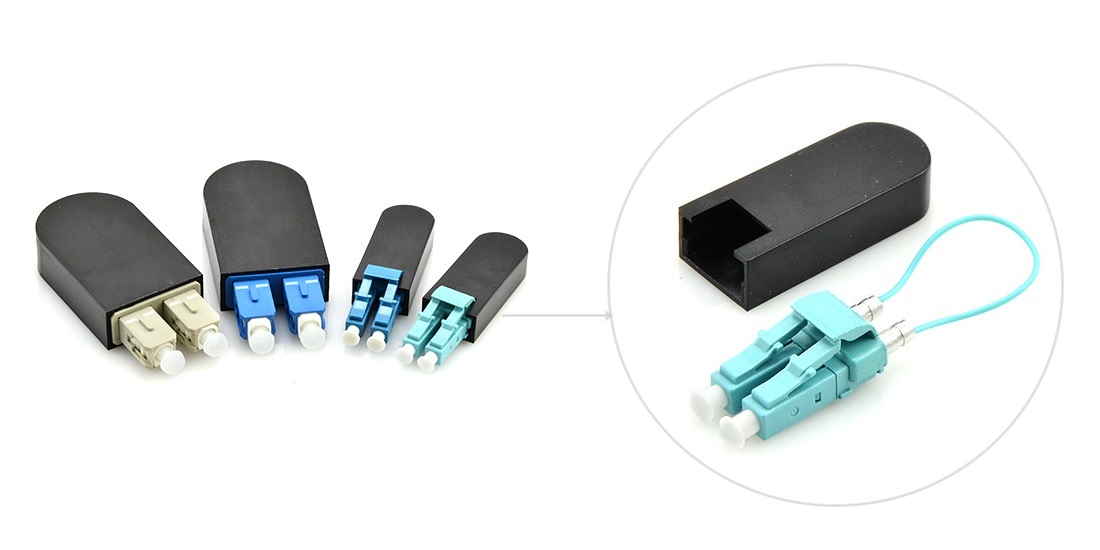

The LC and SC loopbacks are made with simplex fiber cable and common connectors; it’s not difficult to understand their configurations. As for the MTP/MPO loopback, it is mainly used for testing parallel optics, such as 40G and 100G transceivers. Its configuration varies since the fiber count is not always the same in different applications.
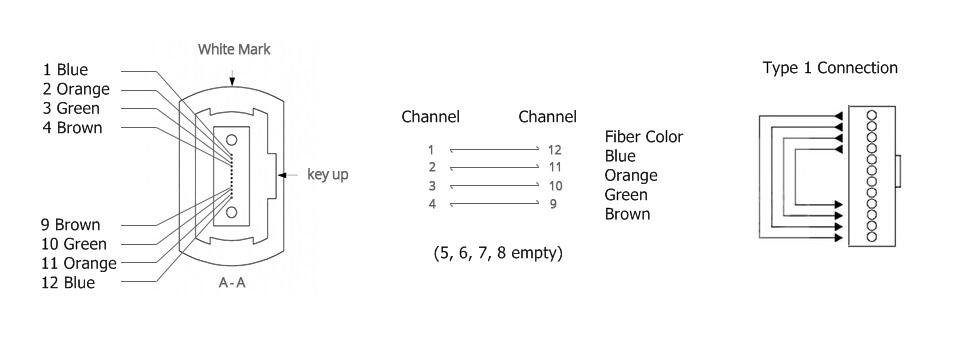
In a 8 fibers MTP/MPO loopback, eight fibers are aligned on two sides of the connector, leaving the central four channels empty. And the fibers adopt a straight configuration of 1-12, 2-11, 5-8, 6-7. The polarity channel alignment is illustrated in the following figure.
The only difference between the 12-fiber MTP loopback and the 8-fiber loopback is that the central four channels are not empty. Its alignment is 1-12, 2-11, 3-10, 4-9, 5-8, 6-7.

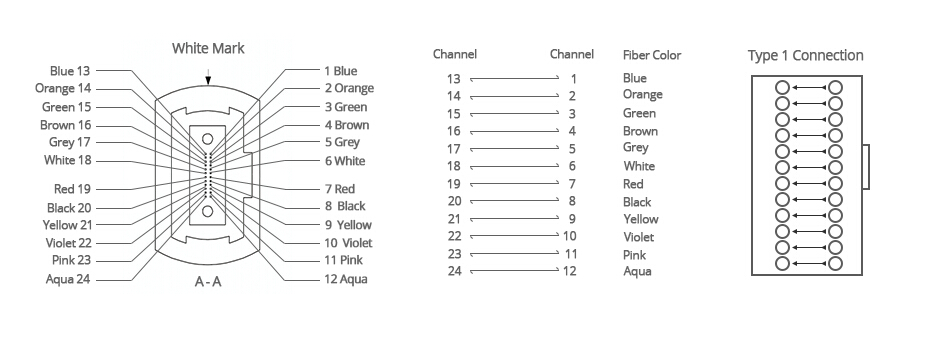
The 24 fibers MTP loopback also adopts type 1 polarity. Its alignment design is shown below.
Considering the common features of the transceiver and the loopback, we should think about the connector type, polish type, and cable type when selecting a loopback for the transceiver. The selection guide for some mostly used transceiver modules is summarized in the following tables.
Table 1: Loopback choices for 10G SFP+ transceivers
| Model | Interface type | Cable Type | Suited Loopback |
| 10GBASE-USR | LC Duplex (PC) | MMF |
LC/UPC Duplex Multimode Fiber Loopback |
| 10GBASE-SR | LC Duplex (UPC) | MMF | |
| 10GBASE-LR | LC Duplex (UPC) | MMF | |
| 10GBASE-ER | LC Duplex (UPC) | SMF |
LC/UPC Duplex Single-mode Fiber Loopback |
| 10GBASE-ZR | LC Duplex (PC) | SMF |
Table 2: Loopback choices for 40G QSFP+ transceivers
| Model | Interface type | Cable Type | Suited Loopback |
| 40GBASE-CSR4 | MTP/MPO (UPC) | MMF |
8/12 Fibers MTP/UPC Multimode Fiber Loopback |
| 40GBASE-SR4 | MTP/MPO (UPC) | MMF | |
| 40GBASE-PLRL4 | MTP/MPO (APC) | SMF |
8/12 Fibers MTP/APC Single-mode Fiber Loopback |
| 40GBASE-PLR4 | MTP/MPO (APC) | SMF | |
| 40GBASE-LR4 | LC Duplex (PC) | SMF |
LC/UPC Duplex Single-mode Fiber Loopback |
| 40GBASE-LR4L | LC Duplex (UPC) | SMF | |
| 40GBASE-ER4 | LC Duplex (UPC) | SMF | |
| 40GBASE-LX4 | LC Duplex (UPC) | MMF/SMF |
LC/UPC Duplex Multimode/Single-mode Fiber Loopback |
Table 3: Loopback choices for 100G QSFP28 transceivers
| Model | Interface type | Cable Type | Suited Loopback |
| 100GBASE-SR4 | MTP/MPO (UPC) | MMF |
8/12 Fibers MTP/UPC Multimode Fiber Loopback |
| 100GBASE-PSM4 | MTP/MPO (APC) | SMF |
8/12 Fibers MTP/APC Single-mode Fiber Loopback |
| 100GBASE-LR4 | LC Duplex (UPC) | SMF |
LC/UPC Duplex Single-mode Fiber Loopback |
Table 4: Loopback choices for CFP transceivers
| Model | Interface type | Cable Type | Suited Loopback |
| 40GBASE-SR4 CFP | MPO/MTP (UPC) | MMF |
8/12 Fibers MTP/UPC Multimode Fiber Loopback |
| 40GBASE-LR4 CFP | SC Duplex (UPC) | SMF |
SC/UPC Duplex Single-mode Fiber Loopback |
| 40GBASE-FR CFP | SC Duplex (UPC) | SMF | |
| 100GBASE-LR4 CFP | SC Duplex(PC/UPC) | SMF | |
| 100GBASE-ER4 CFP | SC Duplex(PC/UPC) | SMF | |
| 100GBASE-SR4 CFP | MPO/MTP (UPC) | MMF |
24 Fibers MTP/UPC Multimode Fiber Loopback |
This post discusses specific fiber loopback choices for some most commonly used fiber optic transceivers. For other transceiver modules that are not mentioned in this post, we can also know how to choose a suitable loopback for it by getting details about its interface type, physical contact and cable type.