The utilization of fiber color code in data center effectively helps technicians make better cable management and reduce human errors. Without redundant checking process, people can easily get the information of the device by only one look. Making good use of the color code system can surely save much time during work. This article will mainly present the widely accepted color code system and its important functions.
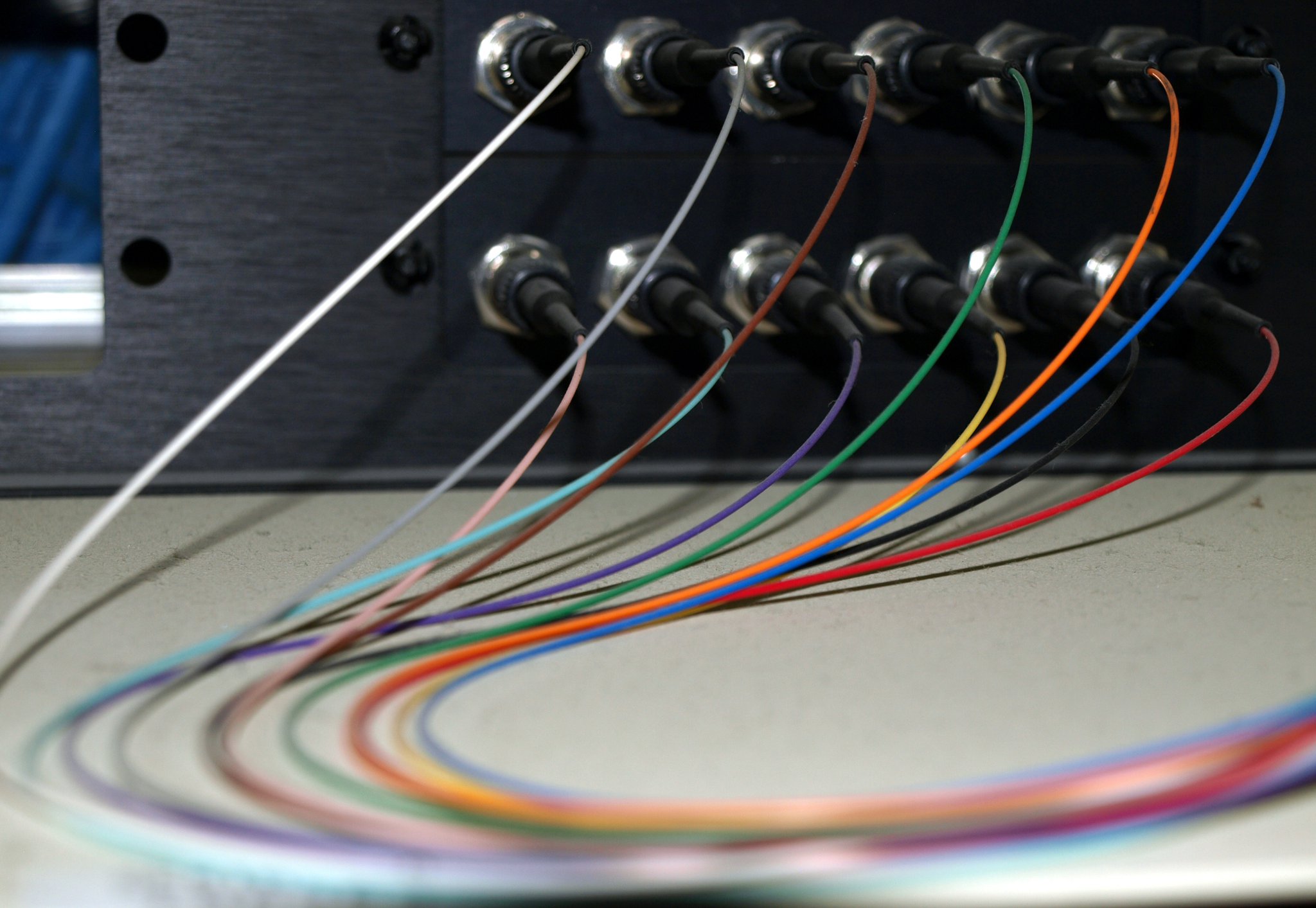
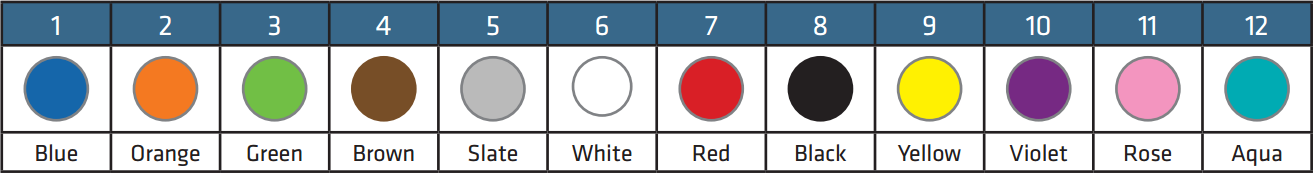
Fibers, tubes and ribbons in fiber optic cables are usually marked with different color codes to facilitate identification. There are many color code systems for national or international use. All these systems are characterized by using 12 different colors to identify fibers that are grouped together in a common bundle such as a tube, ribbon, yarn wrapped bundle or other types of bundle.
Different color code standards may be used in different regions. For example, the S12 standard is used for micro cables and nano cables in Sweden and other countries. The Type E standard is defined by Televerket and Ericsson used in Sweden. The FIN2012 standard is used in Finland, etc. However, there is one color code system widely recognized in the world, namely the TIA/EIA-598 standard.
The following picture gives the fiber color coding of TIA/EIA-598 standard. If more than 12 fibers or tubes are to be separated, the color sequence is normally repeated with ring marks or lines on the colored fibers and tubes. As for the fiber cable jacket, orange, yellow, aqua and black color codes are used for their distinction.
As mentioned above, the outer jacket color codes are able to identify the fiber grades. OM1/OM2 cables often adopt the orange jacket, OM3/OM4 cables with aqua jacket, single-mode cables with yellow jacket and hybrid cables (indoor/outdoor cables and outside plant cables) with black jacket. One thing to note is that the mix of OM1 and OM2 or OM3 and OM4 cables may be troublesome. You should make sure not to mingle these cables with the same color code.
Using fiber color code to label fiber patch cords can reduce the potential for human error. For instance, you may highlight mission-critical patch cords in red, and then teach all technicians that a red patch cord should only be moved with proper authorization or under supervision. Likewise, keeping the fiber connector color consistent with fiber grade color standards will make it simple for technicians to use the right connectors with the cables.
The color-coded port icons can be helpful in identifying different network routings in accordance with internal needs. By tagging each patch panel port, you can simplify and streamline network management.
You can use fiber color code on connector boots to make routine maintenance and moves, adds and changes easier by helping technicians preserve correct parallel groupings for switch ports. If you change your connector color, you need to ensure that your fiber cable color represents the fiber grade to avoid confusion. You can also change the color of a connector boot to differentiate between different aspects of the network, making it easy for technicians to view the contrast within a panel.
Visual management is more intuitive for specialists to supervise the data center. Color code system has provided an ideal and easy way to solve the cabling problem. Inside the cables, the fiber buffers are also color-coded with standard colors to make connections and splices easier. Therefore, if you are still bothered by these issues of fiber patch cables, using the fiber color code system is a good way to go.
Related Articles:
How to Identify the Color Codes?
Fiber Patch Panel Color Codes
