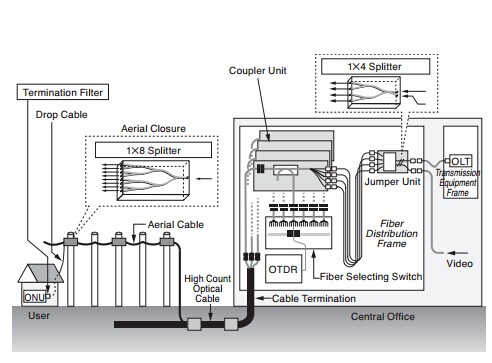
In FTTx and PON architectures, fiber optic splitter is an important component to share the optic network with multiple users. The basic principle of fiber optic splitter is to split one optic light beam into several parts at a certain ratio. According to different manufacture technologies, fiber optic splitters can be divided into PLC splitter and FBT splitter. You may wonder the differences of the two splitter types when making a choice between them. This article aims at helping you to understand their distinctions and make better decisions.
PLC refers to planar lightwave circuit. As a micro-optical device, PLC splitter uses an optical chip to split the input signal into various outputs. At the edge of the chip, there is a light circuit in ribbon form mounted on a carrier and fibers. PLC splitter typically adopts silica glass as the material of lightwave circuit and accepts different types of polished finishes. The substrate, waveguide and lid are three basic layers of the PLC splitter. For different applications, PLC splitters can be further categorized into different types including bare PLC splitters, blockless PLC splitters, ABS PLC splitters, LGX box PLC splitters, mini plug-in type PLC splitters, tray type PLC splitters and 1U rack mount PLC splitters.

FBT, or fused biconic taper uses the traditional technology to fuse several fibers together closely. Fibers are aligned by heating for a specific location and length. Fusion process will not stop until the parameters of the fibers reach the required standards. Since fused fibers are very fragile, they are protected by a glass tube made of epoxy and silica powder. Then a stainless steel tube covers the inner glass tube and is sealed by silicon. FBT splitter with ABS box is also widely used for different applications.

PLC and FBT splitters may look similar to each other, yet they still have many differences when it comes to actual applications. Here will compare them from several aspects.
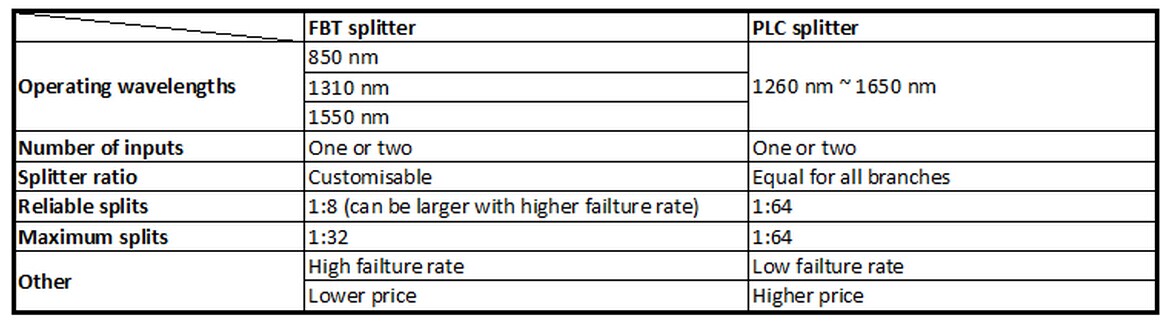
Splitting ratio is decided by the inputs and outputs of a splitter. A PLC splitter is available with the splitting ratio of 1:64, which means one light beam can be separated into 64 splits at a time. However, FBT splitter is typically used for networks requiring the splitter configuration of less than 4 splits. When its splitting ratio is larger than 1:8, more errors will occur and cause higher failure rate. Thus, FBT splitter is more restricted to the number of splits in one coupling.
PLC splitter has a wider operating wavelength ranging from 1260 nm to 1620 nm, thus it can be applied to most of the applications in FTTx and PON networks. On the contrary, FBT splitter has a limitation only to be used for 850nm, 1310nm and 1550nm wavelengths. This leads to the unavailability of FBT splitter on other wavelengths.
Temperature dependent loss (TDL) of the splitter is affected by the manufacturing process and the sensitivity of device. Once the working temperature of splitter is out of range, insertion loss will increase and influence the performance of splitter. PLC splitter is able to work at the temperature of -40 to 85 Celsius degrees while FBT splitter can only work at -5 to 75 Celsius degrees.
Owing to the complicated manufacturing technology of PLC splitter, its cost is generally higher than the FBT type. If your application is simple and short of funds, FBT splitter is definitely a cost-effective solution.
In this article, some differences between PLC and FBT splitters are introduced to help you choose the most suitable one for your network. Overall, PLC splitter has better performance and less limitations, but FBT splitter is less expensive to save more for the budgets. If you are still uncertain which one to choose, please consult a professional for help.