In an era of various services operating, telecom operators will be transformed into the comprehensive service providers of information and communications technology (ICT).The abundant services drive the higher demand for broadband services, directly manifesting the requirement for the ability and performance of the transport network. Owing to meet the needs of all kinds of new services, the Optical Transport Network (OTN) technology comes into being, playing a leading role in the transport network.
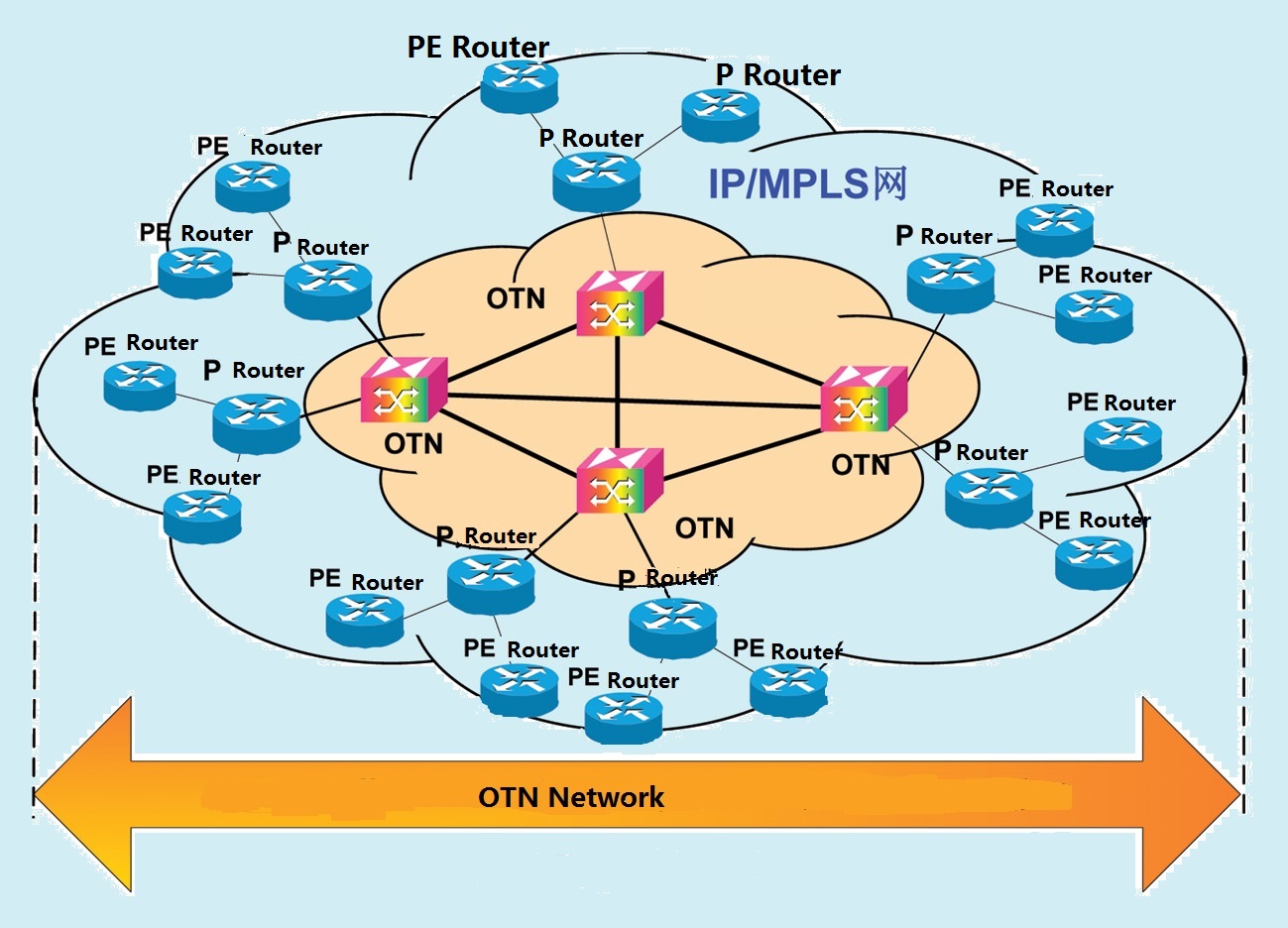
OTN, the next-generation backbone transmission network based on WDM techniques, lies in the optical layer network. Standardized by a series of ITU-T advice covering G.872, G.709 and G.798, it is the new generation of digital transmission network and optical transmission network. OTN is based on a fixed frame size with 3 key sections: Overhead, Payload, and Forward Error Correction (FEC). These OTN frames are routed across the network in a connection-oriented way. Similar to a synchronous digital hierarchy/ synchronous optical network (SDH/SONET) frame, the overhead carries the information required to identify, control and manage the payload to maintain the deterministic quality. The payload is simply the data transported across the network, while the FEC corrects errors when they arrive at the receiver. The number of correctable errors depends on the FEC type. The most common is GFEC described in the G.709 standard, which can identify 16 symbol errors and correct 8 symbol errors per frame. As is shown in Figure 1, the OTN concretely operates as follows. What OTN successfully deals with are the traditional WDM net working issues of missing wavelength, weak scheduling ability of subwavelength services, bad networking ability and poor protection ability. Combining the strength of optical-field handling with that of electrical-field treatment, it is the optimal technology for transmitting the large-particles broadband services, providing the huge transmission capacity, the completely transparent connection of end-to-end wavelength and subwavelength as well as the various protection at telecommunication level.
Figure 1:The operation of an OTN network
The core of most current operator networks is SDH/SONET, which has always offered good fault management, performance monitoring, predictable latency, a protection mechanism and, of course, synchronization. This very stable network has become the expected minimum in performance objectives for network operators today and is often described as having “five 9s” (and higher) performance, meaning at least 99.999% up time. On the basis of the current SDH/SONET managerial functions, ONT provides not only the complete transparency of communication protocols, but also the ability of end-to-end connection and networking for WDM, whose technology inherited the dual advantages of SDH and WDM. It solves the SDH issues that the cross particles based on VC-12/VC4 are too small to meet the transmission requirements of large particles services,causing the complicated schedule. At the same time, it also partly settles the WDM problems of the positioning difficulty due to a system fault, weak networking and poor ability and means to provide the network survivability. OTN reduces transport costs and delivers enhanced network and performance management functions. Forward error correction (FEC) algorithms improve the reach of the transmission links, helping to reduce regenerators and optimize the spectral efficiency. Additionally, an OTN “digital wrapper” includes many layers and components known from SDH/SONET but at enhanced performance levels.
The ever-increasing demand of broadband services has significantly contributed to the application of OTN, which is simpler and better than SDH/SONET and increases the scalability of WDM systems. OTN technology comes into being, not only following the development of the communication technology, but also impelling the transmission network to a better stage. What’s more, the transmission requirements of IP services and the adapter IP services OTN facing has become an important issue that the optical communication further develops. As the optimal choice for developing the transport network, OTN is becoming more and more important, and will be extensively applied to play a dominant role in the transmission network in the future!