Inside plant refers to the cabling running inside a building. Similarly, outside plant is the cabling running outdoors. Outside plant cables are thicker because of more durable insulation jackets. As for fiber optic communication, there are many types of outside plant fiber optic cables. Some have extra protections to prevent corrosion and other elemental interference. Outside plant fiber optics are widely used in telephone networks, CATV, metropolitan networks, utilities and so on. If you want to choose the right outside plant fiber optic cable, its applicable environment is an important factor for consideration. This post will introduce some common outside plant fiber optic cables and typical outdoor application environments.
Several Types of Outside Plant Fiber Optic Cables
Outdoor breakout cable is perfect for rugged applications and installations that require increased performance. It is usually made of several bundled simplex cables wrapped in a common cable jacket. The fungus, water and UV protections and temperature durability are beneficial to its outside applications. Its design of individual fiber reinforcement enables the quick termination to connectors and omits the use of patch panels or boxes. With much less termination work, outdoor breakout cable is more cost-effective when small fiber counts and short distances are required.
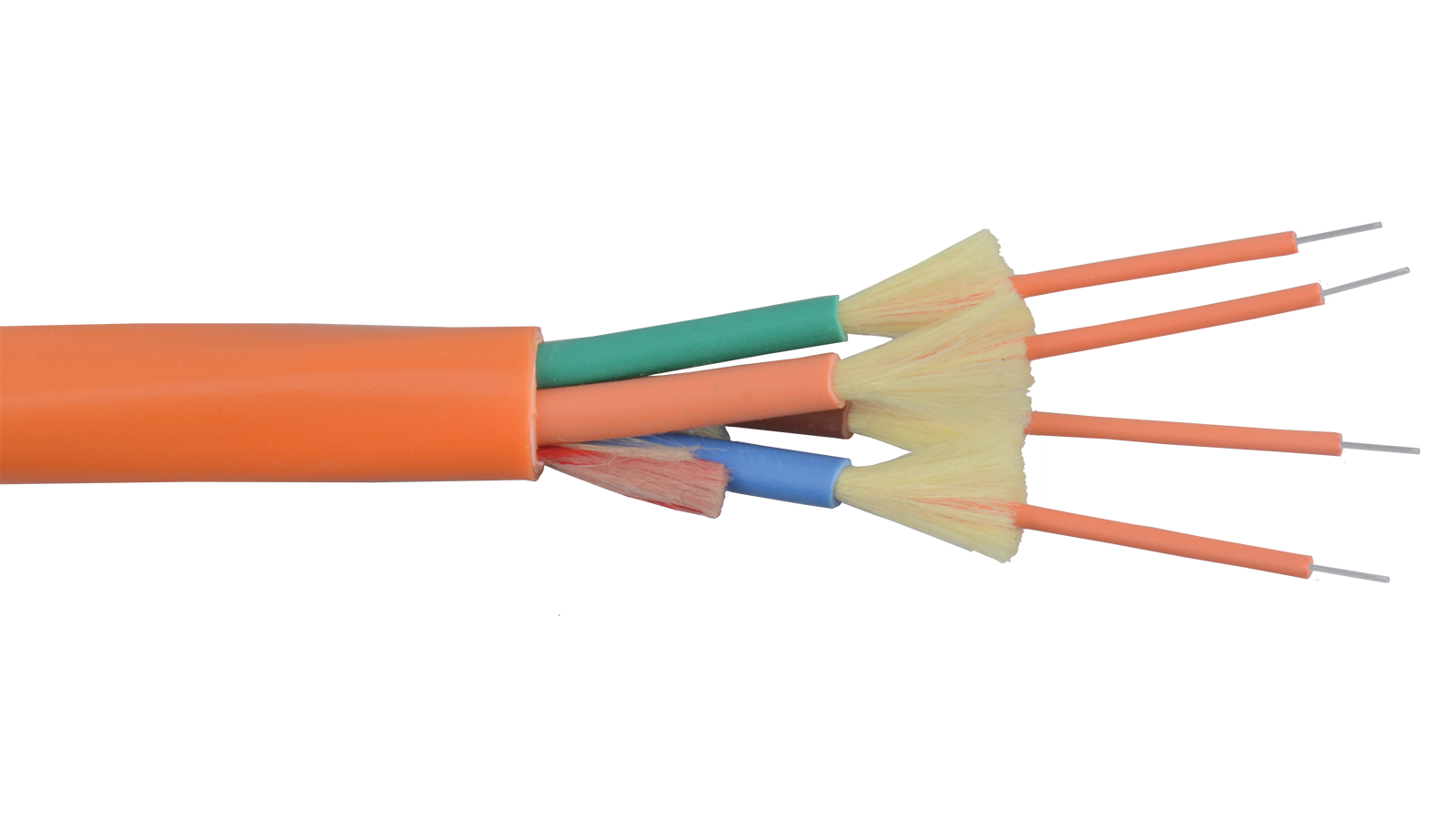
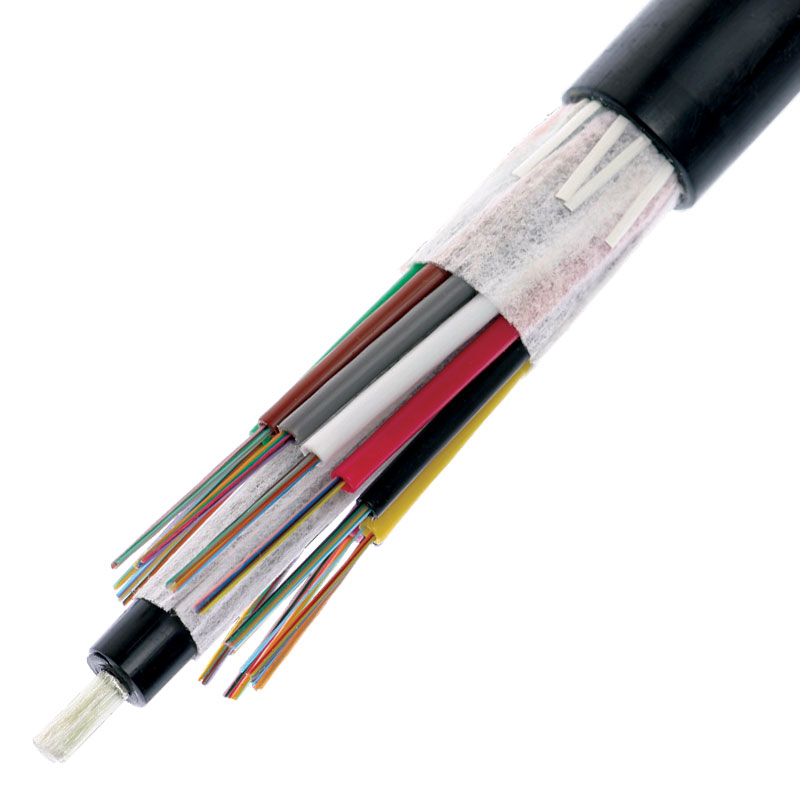
Outdoor loose tube cable has the gel-filled design protecting the cable from moisture environment. The gel within the loose-tube construction stops the penetration of water and keeps it away from the fiber. Also, it keeps water from freezing near the fiber at low temperatures which reduces the chance of stress fractures. Fibers are bundled inside a small plastic tube that can protect fibers from outside stresses. Outdoor loose tube cable is often used in conduits, strung overhead or buried directly into the ground.

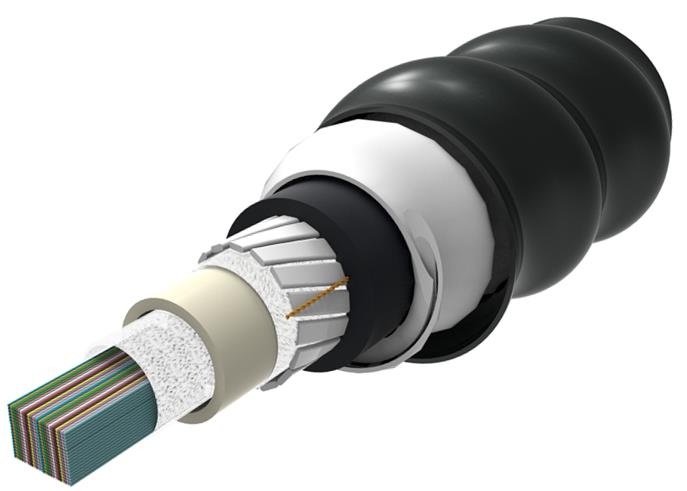
Outdoor ribbon fiber optic cable has high fiber counts and small cable diameter. It contains the most fibers in the smallest cable. These fibers are laid out in rows as ribbons, and ribbons are laid on top of each other. Likewise, it also has gel-filled protection to block outside water. Ribbon cable makes installation much faster and easier since mass fusion splicers can join a ribbon at once.

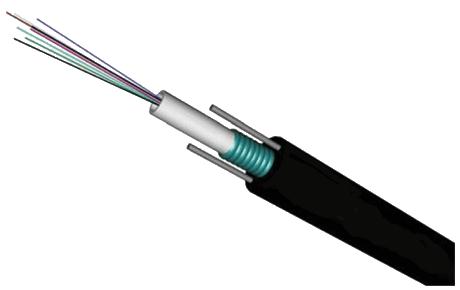
Outdoor armored cable is a direct buried type that prevents itself from animal bite. The metal armoring between two jackets effectively prohibits rodent penetration. Outdoor armored cable can be divided into light armored and heavy armored types. The former has the protective plastic jacket with the same durability and longevity of a stainless steel cable with a lighter weight. The latter is wrapped in a wire circle to be applied for underwater regions that near shores and shoals.
Outside Cable Plant Applications
Outside cable plant deployment can be implemented in many environments. Above-ground, underground, buried and underwater are the typical applications.
Above-ground cable plant can be exposed to extreme temperatures, and to humidity that varies with the seasons and with daily temperature changes. Cables under such circumstances should be durable to adapt to extreme weathers and water penetration.
Underground cable plant usually applies cables in underground structures including the utility holes, controlled environmental vaults, ducts and so on. The condition in utility holes and ducts sometimes can be corrosive because of man-made chemicals. Cables with corrosion-proof materials are perfect for this environment.
Buried cable plant applies cables directly into the soil. Cables can also be exposed to the same corrosive environment as underground plant. But animal bite is an additional problem. Cables for this application should be very tough to endure both chemical corrosion and animal attack.
Underwater cable plant are located beneath the surface of water. The water can range from relatively pure to brackish, or to badly contaminated with industrial effluent. Cables for underwater plant are extremely rugged, with fibers in the middle of the cable inside stainless steel tubes and the outside coated with many layers of steel strength members and conductors for powering repeaters.
Conclusion
Unlike indoor cables, outside plant fiber optic cables must be wrapped in different layers to withstand the severe installation conditions. Choosing the right kind of outdoor cable can save you a great deal for long-term maintenance. And your project application is an important aspect that will affect the selection of fiber optic cables.
Related Articles:
High-Density 40G to 10G Breakout Cabling Solutions
Optimize Network Capacity with Ribbon Fiber Cable
