PoE has gained popularity in a number of applications, including IP cameras, IP phones, and wireless access points, by running power and data transfer over a single Ethernet cable. However, without proper PoE cables, PoE may have cable heating and connectivity problems, which would negatively impact the transmission performance from the PoE switch to these devices. This article will give you some guidance for your Ethernet cable selections in PoE deployment.
Power Over Ethernet Standards
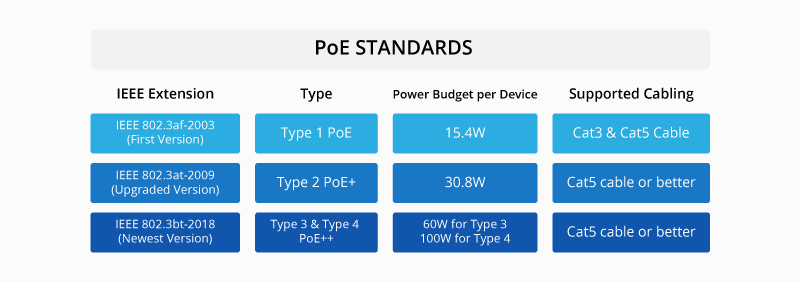
Power over Ethernet (PoE) stands for a proven method of delivering DC power over the same twisted pair cabling used for LAN data transmission. The IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) standards for Power over Ethernet are 802.3af, 802.3at, and 802.3bt presented as follows:
PoE technology allows a single PoE network cable to provide the required communication and electrical power to a variety of devices. Therefore, choosing the right PoE cable is essential for network communication.
Applications Using PoE Ethernet Cables
PoE technology with explosive growth rates has been widely adopted in various applications—PoE IP surveillance cameras, PoE-enabled Voice over IP (VoIP) phones, Wireless Access Points (WAPs), IP PoE-based lighting, Point-of-Sale (PoS), etc. For example, see how FS PoE cables function in a network scenario by connecting FS S3150-8T2FP PoE switch to powered devices (PDs).

Factors to Select PoE Cables
Choosing the right cable is the key to network quality and reliability. What should be taken into consideration when choosing PoE network cables? There are several factors that need to be considered when selecting the cable type used for PoE applications.
Data Transmission Requirements
The first factor to consider is the data transmission requirement (e.g., 1000BASE-T, 10GBASE-T) of the device(s) being utilized. Cat5 cable can be sufficient for PoE protocol short-distance transmission. However, more advanced transmission-grade cables, like 1000Base-T, can be needed for digital devices like high-megapixel IP cameras. Cat6 cable and Cat6a cable are typically utilized for applications that require modest efficiency. To accommodate high-wattage PoE requests, 2.5GB to 5 GB Ethernet data speeds are needed, hence HDBase-T cable is recommended. Cat7 and Cat8 cables are preferred for the most sophisticated, effective applications. The newest and most advanced copper cable type, category 8, offers strong performance and top transfer rates of up to 25 GB across a steady channel.
Conductor Size
Conductor resistance (DCR) in PoE applications results in heat generation in the cable. Typically, Cat6 and Cat7 have larger conductor sizes than Cat5e patch cables. Cables with a larger conductor size can reduce more conductor resistances. Generally speaking, the heat generated in the cable will be reduced with the same ratio of the conductor resistance reduction. Cat6 cables tend to have about 80% of the DCR of Cat5e, thus only about 80% of the heat generation. The larger the conductor size of the cable, the better.
Cable Structure
Cable construction is also a factor causing the temperature rise of a cable. Copper cable can be divided into UTP (unshielded twisted pair cable) and STP (shielded twisted pair cable) two types based on cable structure. Usually, cables with metallic or foil shields are proven to dissipate more heat than UTP cables. Higher heat dissipation leads to cooler cable. When using Cat6 F/UTP cable, more than 40% of the heat can be dissipated compared to Cat6 UTP. If allowed, picking Cat7 S/FTP cable with a foil shield around each pair can dissipate more heat than Cat6 and Cat6 F/UTP.
Further Learning: Shielded vs Unshielded Cat6a: How to Choose?
Cable Temperature
The previous two factors will affect the cable temperature to some degree. Cables with high-temperature ratings allow for a higher amount of power to be dissipated. Typical temperature ratings for cables are 60°C, 75°C, and 90°C. If the temperature of a cable rises, the electrical performance will be degraded. And it’s not good for the cable’s physical performance and longevity. Normally speaking, STP cables are less likely to be affected by temperature than UTP cables.
Cable Materials
When selecting PoE network cables, make sure that you are comparing apples to apples. Copper-clad aluminum vs. pure copper cables, the former uses aluminum instead of copper wire. Some people may choose the copper-clad aluminum cable (CCA cable) on account of the tight budget, which may lead to network issues from using inferior materials to transmit the signal. The CCA cables have much higher DC resistance than copper cables. If the resistance is not compensated, the voltage drop will be greater for any channel length. Longer lengths will exceed TIA’s channel DCR requirements, limiting the voltage available to the device. Higher resistance causes radiant heat to build up faster, and this may cause damage to the device. 100% copper network cabling is a safer and more reliable choice for PoE applications.
Power Consumption
The amount of power that the PoE device requires for operation can’t be ignored when selecting PoE cables. The power requirement will dictate which IEEE standard to follow and what the minimum category cabling to be used. Although each standard regulates a minimum category of cabling, other factors are important to be considered including voltage drop and heat dissipation. Voltage drop determines how much of the supplied power reaches the receiving device. The energy that is lost over the length of the cable transforms to heat and is referred to as heat dissipation. Excessive heat build-up can cause an increase in attenuation as well as premature aging of the cabling jacket.
Installation Configuration
The last factor is the cable installation configuration which has a large effect on the heat dissipation ability. Heat will be kept within the cable as high thermal resistance and high conductor temperature occur with large cable bundles or other installation factors. The larger the cable bundle size, the higher the temperature, no matter what cable category and construction structure. Therefore, to avoid elevated temperatures, avoid environments that may confine heat to the cable, such as large cable bundles, cable bundles close together, and constructions or installations that don’t adhere to approved standards. It is important to have a proper ventilation system in the environment.
Here provides several specific installing tips for PoE cabling:
- Get well-prepared before deploying, and never just wing it.
- Check your network devices to verify that they are PoE compliant.
- Make use of different media in the whole cabling design.
- Do not run cable near devices that generate electrostatics.
- The PoE cable installation is not a one-and-done, please prepare for future upgrades.
- Think about your budget for the whole cabling installation, and find a cost-effective solution from a reliable supplier.
FS: A Trustworthy PoE Cable Supplier
After considering the abovementioned factors, finally, there comes the selection of the network cable provider. High-quality and high-reliability PoE cables are what a qualified supplier should offer. FS encompasses a wide range of high-quality Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, and Cat8 PoE cables with shielded or unshielded type options. All of the Ethernet patch cables have passed strict Fluke tests, including the Fluke patch cord test, Fluke channel test, and Fluke permanent link test to guarantee high performance. FS Assured Program for Ethernet Cables offers more detailed information on FS’s PoE Ethernet cables.
Related Articles:
PoE Cabling Explained: Architectures, Advantages, and Applications
How to Avoid Overheating in PoE Cabling?
Article Source: