Ethernet switches, also known as network switches, serve as the brain of the whole network, especially for data center. On the market, there are various types of Ethernet switches which are designed for different requirements, such as port number, speed, managed or unmanaged. Faced with so many choices, you may get confused about which one is the best switch. In fact, not just you, there are a lot of people who don’t know how to make the choice. In the year 2017, Gigabit switch has been the hot topic at several big forums, and the question “Can you recommend a Gigabit switch for me?” frequently occurred. This article will focus on Gigabit switch review and recommend several Ethernet switches for you.
Gigabit Switch Review 1: D-Link DGS-1008G Gigabit Switch
D-Link DGS-1008G Gigabit switch has eight gigabit ports and boasts data transfer speeds of up to 2000 Mbps. It comes with QoS features, which automatically organize and prioritize important and time-sensitive data packets, ensuring efficient delivery. This feature helps enable smoother media streaming, VoIP calling and online gaming features. In addition, it utilizes D-Link’s Green Technology which allows the switch to reduce heat and use less energy. D-Link DGS-1008G Gigabit switch is a solid choice if you are looking for a fast, easy-to-use and reliable network switch.
Gigabit Switch Review 2: FS S5800-8TF12S Managed Switch
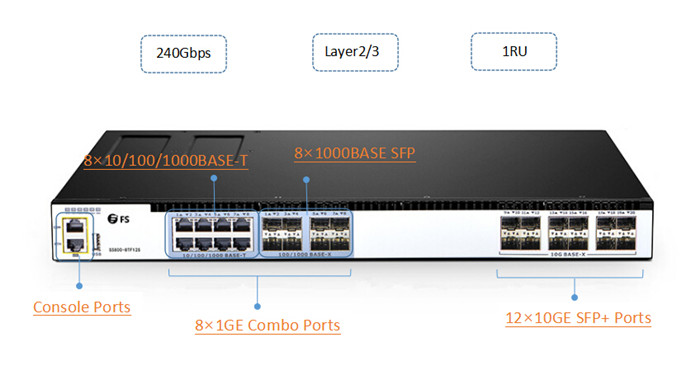
FS S5800-8TF12S switch is a 12 port smart managed switch. It is designed with twelve 10G SFP+ ports and eight 1000BASE-T/ SFP combo ports. The 1000BASE-T copper RJ45 ports support Gigabit speeds over Cat6 cable up to 100 meters, and the 1G SFP fiber ports can be connected to other devices via SFP transceivers over fiber optic cable. FS S5800-8TF12S 12 port smart managed switch is designed to support a demanding and dynamic environment of SMB networks. It is a good choice for 10G access Layer switch for hyper-converged infrastructure.
Gigabit Switch Review 3: UniFi US-24-500W PoE Switch
UniFi US-24-500W switch is a 24 port PoE switch which comes with 24 Gigabit RJ45 ports and 2 SFP ports. Its non-blocking throughput is up to 26 Gbps and the switching capacity is up to 52 Gbps. UniFi US-24-500W PoE switchh is a fully managed Gigabit switch which can deliver robust performance and intelligent switching for networks. Besides, it offers the forwarding capacity to simultaneously process traffic on all ports at line rate without any packet loss. It is really a cost-effective PoE switch at $399.00. For more details about Gigabit PoE switch review, you can read my previous article: 8 Port PoE Switch Recommendations.
Gigabit Switch Review 4: FS S5850-48T4Q 10GBASE-T Switch
FS S5850-48T4Q 10GBASE-T copper switch is a 1U managed L2/L3 Ethernet switch. It has forty-eight 10GBASE-T RJ45 ports and four 40G QSFP+ ports. And it can provide 1.28Tbps switching capacity. FS S5850-48T4Q switch is designed to meet next generation Metro, Data Center and Enterprise network requirements. For example, it can be used for Spine-Leaf network which is a popular architecture design for data center. For 1GBASE-T copper switch at lower cost, FS S5850-48T4Q switch is a great option to help you migrate to 10GbE network.
Conclusion
The above content Gigabit Ethernet switch review has recommend 8 port unmanaged Gigabit switch, 12 port 10G smart managed switch, 24 port PoE switch and 48 port 10GBASE-T copper switch. All of them are good choices when compared with the same type of Ethernet switches. I hope this article can help you choose the best switch when you feel confused.
Related Article: FS 1000BASE-T Gigabit Switch: S3800-24T4S vs. S3800-48T4S