As communication technology develops rapidly, the demand for higher bandwidth is increasing. To solve this problem, optical cable is widely used as the backbone of communications network cabling, especially in big data center. In recent years, projects like FTTH (Fiber to the Home) and FTTB (Fiber to the Building) are carried out to provide better services for customers. To future capitalize on the benefits of optical cable, Fiber to the Desk (FTTD) is recommended for enterprises, financial institutions and federal agencies, which need high security and high data transmission speed. This article will guide you to have a closer look at application of FTTD.
FTTD refers to the extension of the fiber optic infrastructure directly to user locations, just as the following figure show, optical cables are directly connected to desktops, laptops, or other communications equipment. FTTD can be used for virtual networks using thin clients and LAN networks with extended distances to workstations. It can satisfy the requirement for increasing bandwidth availability, moving large amounts of data at high transmission rates. In addition, it is able to bring service to locations where power is limited or unavailable as well as provide a more secure connection for organizations who are concerned about tapping or other security vulnerabilities.
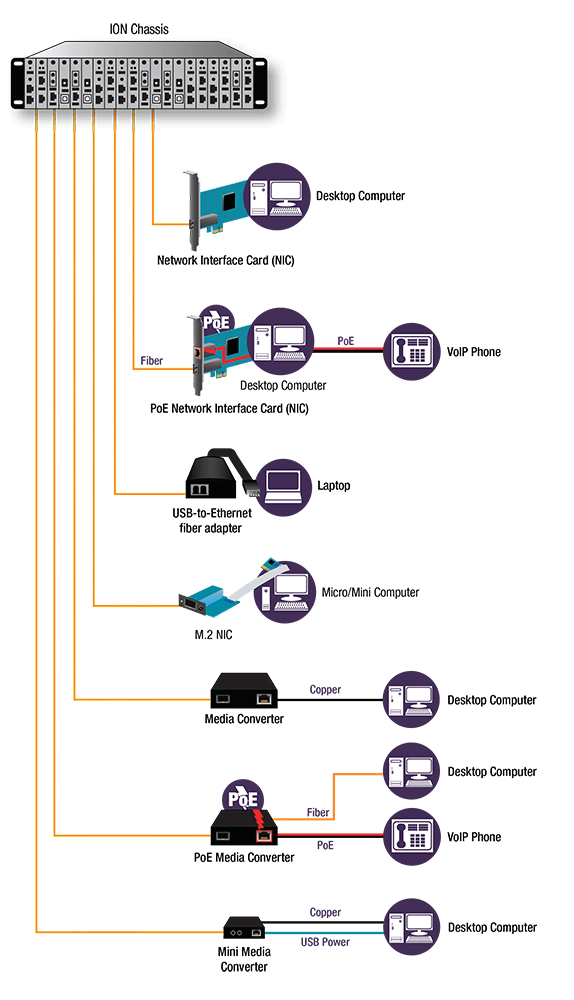
We know that RI45 Ethernet cable can also be used as transmission media. What makes optical cable superior to RJ45 Ethernet cable? This part will show you the advantages of using optical cable for FTTD project.
Optical cable is immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI), so it is more difficult for hackers to tap on optical cable. Besides, optical cable uses light that is completely shielded, so hackers would have to physically splice into the line, which is difficult to do and easily detected. While RJ45 Ethernet cable emits electromagnetic signals which allows hackers to read data from nearby without physically touching the lines. In contrast, optical cable is a more secure option for applications concerned with data security.
Optical cable is able to support higher data rates than any other cable type, with capacity to transmit up to 100 Gbit/s. As demand for higher bandwidth is ever-growing, optical cable has the absolute advantage. What’s more, connected with appropriate optics, the transmission distance of optical cable can reach dozen kilometers. Although higher grades of RJ45 Ethernet cables can transmit 10G data signals, they will only be able to do so over very short distances. Therefore, optical cable is the best choice for transporting higher speed and higher bandwidth signals over longer distances.
Optical cable used to be more expensive than RJ45 Ethernet cable. As demand has increased, manufacturing costs have dropped. Also, if properly designed, the FTTD project could be affordable. Apart from this, optical cable can ensure your network cabling can keep up with the growth in network traffic over time and upgrade your network to higher bandwidth in the future without recabling. Considering the cost of cabling, this can be a huge advantage. Though the initial cost of fiber equipment may be slightly higher than copper, the benefits realized can save organizations significant cost in the long term.
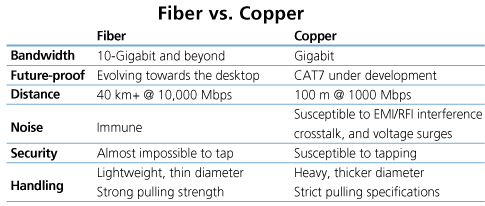
Optical cable Vs. RJ45 Ethernet cable
FTTD is a high-bandwidth solution that expands the traditional fiber backbone system by running fiber directly to desktops. FTTD is a horizontal wiring option that pushes the available bandwidth beyond 10G. It is an intriguing, underestimated and overlooked way to create a beneficial system that is expandable and performance-driven. The optical cable, fiber optic wall plate, PoE media converter and some other fiber optics used in FTTD are available in FS.COM. For more details, you can visit our site.
