Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is one of the most recent and important technologies in the development of fiber optic transmission technology. Its most obvious advantage is the ability to provide potentially unlimited transmission capacity. In a DWDM system, there are four important components, which are optical transmitter/receiver, DWDM Mux/Demux filter, optical add/drop multiplexer (OADM) and optical amplifier. This article will give an introduction to these four components respectively.
Optical Transmitter/Receiver
As a highly important part of the DWDM system, the optical transmitter/receiver is responsible for providing source signals and receiving signals. Multiple optical transmitters are used as the light sources in a DWDM system. The lasers on the transmit side create pulses of light. Each light pulse has an exact wavelength which shall be precise and stable.
As the development of fiber optic transmission technology, the optical transmitter/receiver has been gradually replaced by the optical transceiver. Optical transceiver is a device comprising both a transmitter and a receiver which are combined and share common circuitry or a single housing. There is another device named transponder used in the DWDM system sometimes. It has the similar principle with the optical transceiver. Both optical transceivers and transponders have the function of optical-electrical-optical (O-E-O) conversion. The main difference between them is that the interface of optical transceivers is serial, while the interface of transponders is parallel.
DWDM Mux/Demux Filters
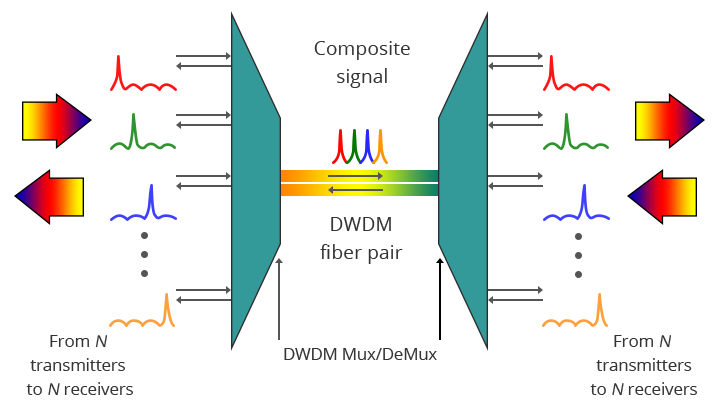
It is known to us that multiple wavelengths created by multiple transmitters operate on different fibers. The role of optical filter (multiplexer filter) is to combine these multiple wavelengths onto one fiber. The output signal of an optical multiplexer is referred to as a composite signal. Then an optical drop filter (demultiplexer) at the receiving end performs the function of separating out all the individual wavelengths of the composite signal to individual fibers. One thing needed to be noted is that the demultiplexing process should be done before the light is detected. The following figure shows a bidirectional DWDM operation. N light pulses of N different wavelengths carried by N different fibers are combined by a DWDM Mux. A DWDM Demux receives the composite signal and separates each of the N component signals and passes each to a fiber.
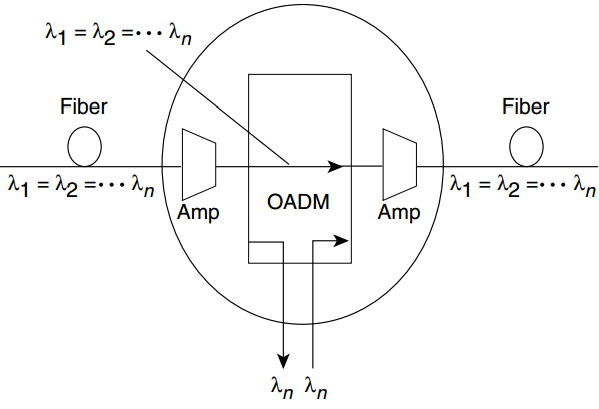
DWDM OADM
In the DWDM system, there is an area in which multiple wavelengths exist between multiplexing and demultiplexing points. And it is desirable that one or more wavelengths at some point along this span can be added or dropped. The OADM is designed for this function. Rather than combining or separating all wavelengths, the OADM can remove some of the wavelengths and allow the other wavelengths to pass on. The following figure shows the add-drop process of OADM (“Amp” represents for amplification, “λ” represents for wavelength).
Optical Amplifier in DWDM System
Since the DWDM system is for long transmission links, the signals must be amplified after a certain fiber length. As a kind of “in-fiber” device, optical amplifier boosts the amplitude or add gain to optical signals passing on a fiber through the way of directly stimulating the photons of the signal with extra energy. Optical amplifier can amplify optical signals across a broad range of wavelengths, which is very important for DWDM system application. The commonly used in-fiber amplifier is erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA).
Continuing to provide the bandwidth for large amounts of data, DWDM system is now becoming the basis of all-optical networking with wavelength provisioning and mesh-based protection.
Related Articles:
Why Is EDFA (Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier) Essential To DWDM Systems?
DWDM Solutions for Metropolitan Area Network