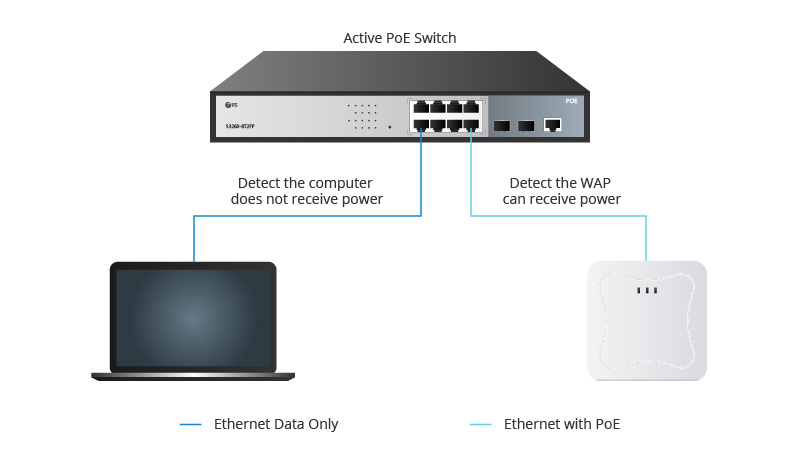
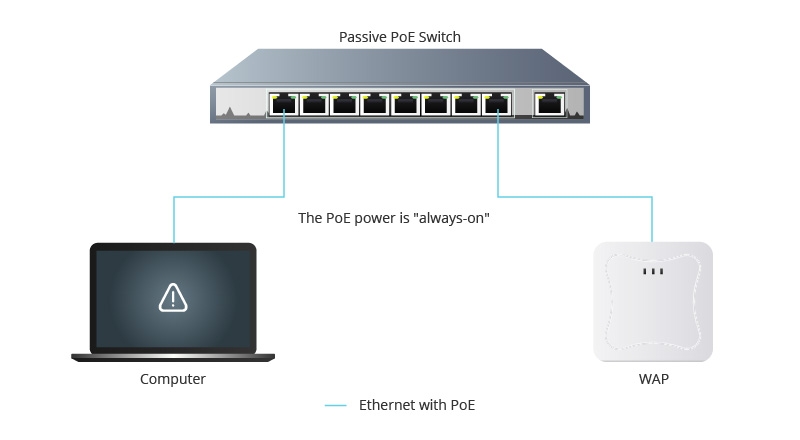
Unlike traditional fan-cooled PoE switch designs, fanless PoE switches discard the conventional air-cooling system in favor of a quieter and more efficient fanless design. This type of switch achieves silent operation through clever passive cooling, maintaining performance without impacting noise levels. If you need to deploy a switch in a quiet and low-dust environment, consider exploring fanless PoE switches.
What is Fanless PoE Switch?
A fanless PoE switch, as the name suggests, is a PoE switch designed without internal fans. It relies on passive cooling through ventilation holes, resulting in a more compact structure compared to fan-equipped switches. The absence of internal fans not only ensures silent operation but also leads to a significant reduction in power consumption. This design minimizes the risk of mechanical failures, enhancing the overall reliability and durability of the equipment. Additionally, it effectively reduces maintenance requirements and operational costs associated with network devices.
The fanless design, characterized by its noise-free, low-power, and environmentally friendly attributes, finds versatile applications in industrial and commercial settings globally. This is particularly true for sensitive environments such as healthcare systems, educational institutions, and commercial offices, where a silent design is paramount.
The Advantages of Utilizing Fanless PoE Switches
Silent Operation for Serene Workspaces
One of the most prominent features of fanless PoE switches is their silent operation. These switches incorporate a fanless design, guaranteeing noise-free performance and fostering a serene network environment in the workplace. This quality proves especially advantageous in settings where maintaining a peaceful atmosphere is crucial. Be it in offices, educational institutions, or other noise-sensitive locations, fanless PoE switches provide a distinct benefit by sustaining network functionality without causing unnecessary disturbances.
Energy-Efficient Contribution to Sustainability
Fanless PoE switches contribute to environmental conservation and sustainability through their energy-efficient features. Utilizing natural convection for cooling and with the absence of internal fans, silent operation is ensured while energy consumption is significantly reduced, resulting in a minimal impact on power costs. The pivotal role of this energy efficiency lies in diminishing the environmental footprint, presenting businesses with an economically viable option as they actively pursue sustainable development.
High-Power Output for Device Support
Fanless PoE switches provide robust power output, ensuring reliable power supply for various devices. Each port can deliver a high power output of up to 30W, making it an ideal choice for high-power devices such as IP cameras, wireless access points, and IP phones. For instance, the FS S3150-8T2FP fanless PoE switch has a total PoE power budget of 130W, allowing the connection of up to 4 PoE+ devices.
Enhanced Stability through Fanless Design
In addition to reducing noise, fanless design in PoE switches enhances stability by minimizing mechanical components. With no mechanical movement, these switches exhibit lower failure rates, ensuring a more stable and reliable operation. In critical network environments requiring prolonged stability, fanless PoE switches provide a robust solution, maintaining network continuity and minimizing potential failure risks.

How to Choose a Fanless Switch?
When selecting a fanless switch, consider the following aspects:
Noise Requirements: If the working environment demands low noise levels, such as in offices, healthcare facilities, or quiet industrial settings, opting for a fanless switch design is a prudent choice to ensure silent operation.
Reliability: Fanless designs typically reduce mechanical movement, lowering failure rates and enhancing equipment reliability. This is crucial for critical networks that require stable operation.
Environmental Suitability: Consider the placement environment of the switch. In industrial settings with higher dust levels, a fanless design can reduce the risk of dust entering the equipment, thereby improving durability.
Power Consumption: Fanless designs usually result in lower power consumption, contributing to energy efficiency. This can be a significant consideration for enterprises aiming for eco-friendly practices.
FS has a variety of fanless PoE switches that meet the above characteristics, such as the FS S3150-8T2FP. This fanless PoE switch operates silently, ensuring a calm network environment. It features 8 RJ45 ports supporting 802.3af/at and automatic PD device detection, delivering up to 30W per port. With PoE capabilities, the S3150-8T2FP efficiently powers PD devices like IP phones, wireless access points, and conference cameras. And it incorporates features such as ACL, QinQ, and QoS. This fanless PoE switch offers a straightforward management interface and flexible installation, with a compact and cost-effective solution.
| Switches | S3150-8T2FP | S3410-10TF-P | S1900-16TP |
| Ports | 8x 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45 | 2x 1G SFP | 10x 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45 | 2x 1G SFP | 16x 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45 |
| PoE Standard | IEEE 802.3af/at | IEEE 802.3af/at | IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3u, IEEE 802.3ab, IEEE 802.3x |
| PoE Budget | 130W | 125W | 135W |
| Protocol | ACL, QinQ, QoS, QoS | ERPS, LACP, QoS, | Auto MDI/MDIX |

Summary
In conclusion, the distinctive design of the fanless PoE switch addresses the issues of noise and mechanical movement associated with traditional fans, showcasing outstanding performance and reliability in diverse environments. The adoption of this technology provides more flexible options for offices, industrial settings, and other network deployments, delivering a quieter and more reliable network experience for users. If you need a PoE switch with good performance and quiet operation, FS fanless PoE switch will give you an excellent user experience.
Related Articles:
FS Unleashes Open Network Switches, Powering Intelligent Networks Forward