As we know, the server rack can organize numbers of network equipment into standard-sized rack, which greatly improves the working and management efficiency throughout the data center. Meanwhile, with the 5G IoT era approaching, more and more intelligent home appliances gradually enter our lives. People especially the IT men desire to use a centralized management to run these equipment. Of course, the best solution is the home server rack. But how much do you know about home server rack setup?
Figure 1: Intelligent Life is Coming.
What Can I Do With Home Server Rack?
Home server rack is the centralized point in your house where the wiring meets switches, routers etc. The most obvious thing that we can do with home server rack is protecting our hardware. Mounting them into the rack instead of putting them on or under a desk can avoid the risk of getting knocked over, having water or other liquids spilled on them. Besides, for the IT passionate and technology enthusiasts, they can use home server rack to build a small data center. With this, they can control and add whatever they please, like installing some game servers and email server in the meantime. So they can build their own services and have fun in running the services.
Considerations of Home Server Rack Installation Guide
As for the home server rack build, here are two aspects that must be considered so as to make sure everything goes smoothly.
Equipment numbers. Before you start the home server rack setup, you should take an inventory of your equipment such as switches, routers. Only know the specific numbers, we can determine the home server rack size. And here I suggest leaving some extra rack space, which is beneficial for cables go through the patch panel rack.
Rack location. We should determine the rack location based on convenience and available space. Because all the interior wiring like Cat5e, Cat6 for network and coax for television may join the home rack. Besides, an airy room is good for rack cooling. Thus choosing the right place in your building is critical.
How to Set Up a Server Rack?
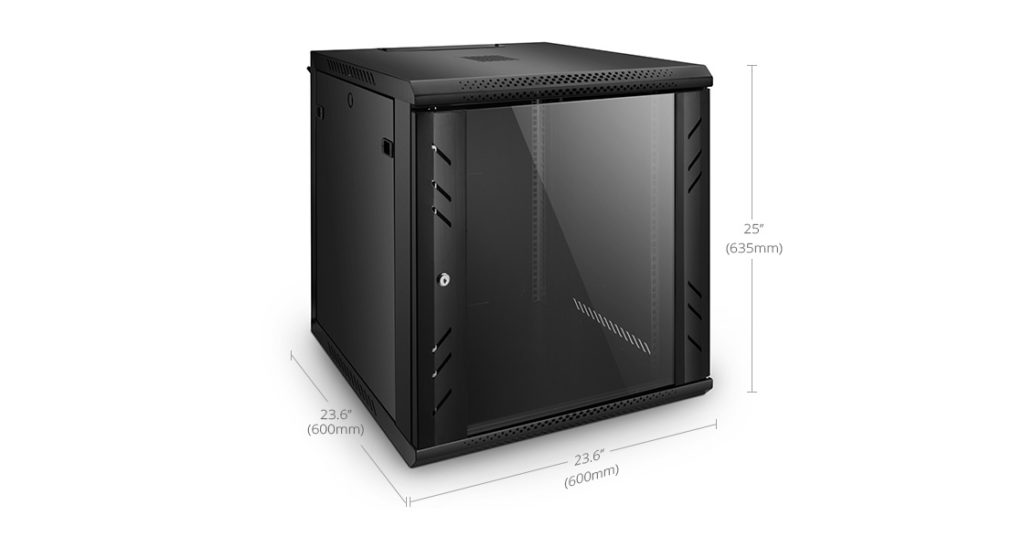
Unlike the racks in the server room, there is no need to use a large server rack at home. So some people are fond of DIY. But I think to make a server rack may spend lots of time and energy. And most of them use the wood as the main material, which is not good for protecting the environment. Here I recommend the 12U server rack from FS.COM to you. Only cost 110 dollars, you can get a server rack that can be mounted on walls and placed on floors. It uses SPCC cold roll steel, which is more sturdy and durable than the wood ones. This equipment is specially designed with glass door to offer a better protection for your network devices, and cooling vents on the back to ensure airflow.
Figure 2: Server Rack for Home
Now, we can place the 12U home server rack in the determined location. Then mount your various devices into the rack. If you have a budget for cable management tools, you can buy a keystone patch panel to manage your cables on racks. Thus, a home server rack setup has been established, you can manage your home network devices conveniently and enjoy the customized services.
Conclusion
Home server rack brings many advantages which may make your life a lot easier and intelligent. After all the work in home server rack setup, you can pride yourself in the creation and effort. So let’s design a home server rack, and start our smart life.