The rise of the digital economy has promoted the rapid and vigorous development of industries like cloud computing, Internet of Things, and big data, which have put forward higher requirements for data centers. The drawbacks of traditional data centers have emerged gradually, which are increasingly unable to meet the needs of the market. The prefabricated containerized data center meets the current market demand and will usher in a period of rapid development.
What Is a Containerized Data Center?
A containerized data center comes equipped with data center infrastructures housed in a container. There are different types of containerized data centers, ranging from simple IT containers to comprehensive all-in-one systems integrating the entire physical IT infrastructure.
Generally, a containerized data center includes networking equipment, servers, cooling system, UPS, cable pathways, storage devices, lighting and physical security systems.
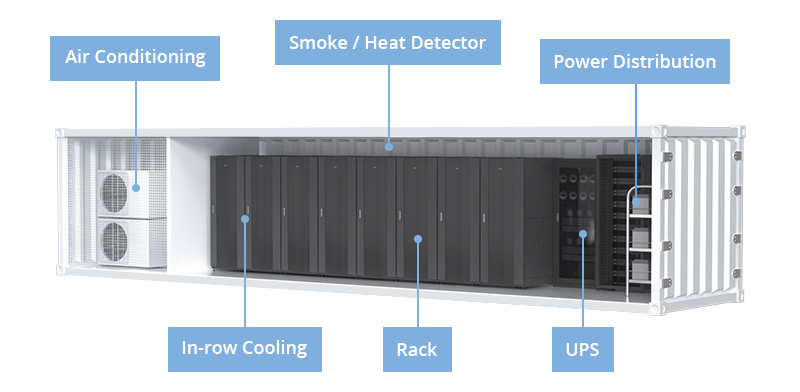
Pros of Containerized Data Centers
Portability & Durability
Containerized data centers are fabricated in a manufacturing facility and shipped to the end-user in containers. Due to the container appearance, they are flexible to move and cost-saving compared to traditional data centers. What’s more, containers are dustproof, waterproof, and shock-resistant, making containerized data centers suitable for various harsh environments.
Rapid Deployment
Unlike traditional data centers with limited flexibility and difficult management, containerized data centers are prefabricated and pretested at the factory, and are transported to the deployment site for direct set-up. With access to utility power, network and water, the data center can work well. Therefore, the on-site deployment period for containerized data centers is substantially shortened to 2~3 months, demonstrating rapid and flexible deployment.
Energy Efficiency
Containerized data centers are designed for energy efficiency, which effectively limits ongoing operational costs. They enable power and cooling systems to match capacity and workload well, improving work efficiency and reducing over-configuration. More specifically, containerized data centers adopt in-row cooling systems to deliver air to adjacent hotspots with strict airflow management, which greatly improves cold air utilization, saves space and electricity costs in the server room, and reduces power usage efficiency (PUE).
High Scalability
Because of its unique modular design, a containerized data center is easy to install and scale up. More data centers can be added to the modular architecture of containerized data centers according to the requirements to optimize the IT configuration in a data center. With high scalability, containerized data centers can meet the changing demands of the organization rapidly and effortlessly.
Cons of Containerized Data Centers
Limited Computing Performance: Although it contains the entire IT infrastructure, a containerized data center still lacks the same computing capability as a traditional data center.
Low Security: Isolated containerized data centers are more vulnerable to break-ins than data center buildings. And without numerous built-in redundancies, an entire containerized data center can be shut down by a single point of failure.
Lack of Availability: It is challenging and expensive to provide utilities and networks for containerized data centers placed in edge areas.
Conclusion
Despite some shortcomings, containerized data centers have obvious advantages over traditional data centers. From the perspective of both current short-term investment and future long-term operating costs, containerized data centers have become the future trend of data center construction at this stage.
Article Source: What Is a Containerized Data Center: Pros and Cons
Related Articles:
